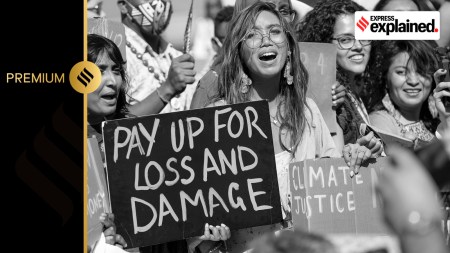EXPLAINED CLIMATE NEWS - Page 12
COP28 begins today: India’s role at the climate conferences over the years, key promises, red linesSubscriber Only
As a large economy and the third-largest emitter of greenhouse gases, India is an influential voice for developing countries at the annual COP events. Over the years, New Delhi has become more assertive and proposed some key measures. Here's a look.
What explains the unseasonal rains and lightning strikes in Gujarat?Subscriber Only
At least 27 people have died due to recent lightning strikes in the state. The IMD has attributed the flashes to three weather systems. We explain how this has contributed to heavy rains in parts of northwestern India.
COP, carbon market, loss and damage: A glossary of climate termsSubscriber Only
The 28th edition of the Conference of the Parties (COP) will begin in Dubai on November 30. Here is a look at the key terms that you might come across.
Five things you need to know about Conference of the Parties (COP), the world’s biggest climate meetingSubscriber Only
COP 28: The annual conference takes place to discuss a global agreement to cut emissions of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the main reason why average global temperatures have been rising.
How the Gulf is planning for a life after oilSubscriber Only
The Gulf countries are marching ahead with an ambitious domestic transition to renewable energy. But there is little chance they will stop exporting fossil fuels any time soon.
Ahead of the COP 28 summit, have we lost the fight against climate change?Subscriber Only
Emissions are rising, there's not enough money to deal with a worsening climate, and its harmful effects become more apparent every day. What's the way ahead?
COP28 in Dubai: What to expect from the climate meetingSubscriber Only
The World Meteorological Organisation says one of the next four years — perhaps 2023 itself — will almost certainly breach the 1.5 degree Celsius threshold.
Why water reserves in southern India are fast depleting in 2023Subscriber Only
October over southern peninsular India remained the sixth driest in 123 years. The collective reservoir stocks have already fallen below 50 per cent in November. Why has this happened and what could the impact be?
What a US-China climate deal means for COP28Subscriber Only
The deal comes at a pivotal moment for the United States, the biggest climate polluter in history, and China, currently the largest polluter. Together, they account for 38% of the world’s greenhouse gases.
How climate change is displacing animalsSubscriber Only
Climate change-linked extreme weather events have become more common as well as more severe. A study sheds light on their profound impact on ecosystems, especially on native species.
Delhi chokes on pollution: What is AQI — and how is it measured?Subscriber Only
The air quality in Delhi has plummeted to hit the ‘severe’ category for the first time this season, with the AQI breaching the 400 mark.
Why a ‘normal’ monsoon isn’t normal anymore for IndiaSubscriber Only
This is the eighth year in a row that monsoon rainfall in India has been broadly in the normal range. But behind this figure lie sharp regional as well as daily variations. Climate change is one reason behind this
What the rapid ice melt in West Antarctica meansSubscriber Only
The rapid melting of ice sheet in West Antarctica is now unavoidable, according to a new study. What is an ice sheet? Why does its melting matter? Is all hope lost?
Why Mumbai is witnessing more poor air quality daysSubscriber Only
Sea breezes in coastal Mumbai long protected its air quality. But since last year, this geographical advantage is weakening. In part, this is because of local weather conditions. The bigger issue, however, is the rising pollution.
Severe drought grips the Amazon rainforest: The impact, cause and grim futureSubscriber Only
Hundreds of fish dead, no drinking water, food or other supplies — the latest spell of drought in the Amazon rainforest has disrupted the lives of tens of thousands of Indigenous people. What's the cause behind it?
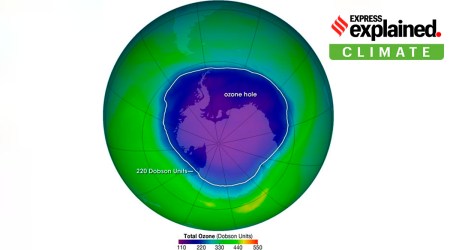
Large ozone hole detected over Antarctica: Is it a matter of concern?Subscriber Only
The ozone hole over Antarctica is one of the biggest on record, roughly three times the size of Brazil. It's a natural phenomenon, but scientists are concerned climate change could begin reopening ozone holes.
What the hottest September ever reveals about climate changeSubscriber Only
September joins several other months of 2023 in breaking temperature records. Why has this year been so warm, and what is expected in the months ahead?
Why India is launching a national framework for climate servicesSubscriber Only
Spearheaded by the IMD, the National Framework for Climate Services will allow India to meet the ever rising challenges posed by climate change.
Glacial lake outburst flood kills 14 in Sikkim, 102 people missing: What is GLOF, and why does it happen?Subscriber Only
Flash floods occurred in north Sikkim after the South Lhonak Lake burst due to incessant rains. For years, numerous studies highlighted the lake’s rapidly growing size and marked it as susceptible to glacial lake outburst flood.
An Expert Explains: In alarm over Conocarpus trees, echo of faulty policies on invasive exoticsSubscriber Only
Suresh Babu, Professor at the School of Human Ecology and Director of the Centre for Urban Ecology and Sustainability at Dr B R Ambedkar University, Delhi, provides insights on the selection of plant species employed in greening projects in India.
An expert weighs in | ‘Earth is now well outside of the safe operating space for humanity’Subscriber Only
A new study has found that most of the planetary boundaries have been breached because of human activities. Katherine Richardson, professor of biological oceanography at the University of Copenhagen and lead author of the study, answers five questions about planetary boundaries and their significance.
Earth has ‘high BP’: Why humans breaching most of the planetary boundaries mattersSubscriber Only
Out of the nine planetary boundaries, humans have breached six. It means Earth’s life-support systems have been driven far away from the safe operating space for humanity that existed during the Holocene period.
Eight countries witness devastating floods in Sept: Is climate change causing deluge across the world?Subscriber Only
A Mediterranean storm called Daniel led to floods in Libya, Greece and Turkey, and other similar events were witnessed in Brazil and China. While it can be tempting to see the deluge in different regions as a direct consequence of climate change, confirming its role in such phenomena is a tricky endeavour.
G20 meet’s climate action promise of tripling global renewable energy capacity by 2030, explainedSubscriber Only
G20 countries have committed to work towards tripling global renewable energy capacity by 2030. Several challenges make achieving the target difficult.
The climate crisis is here: Three climate records the world smashed this yearSubscriber Only
So far in 2023, the world has witnessed the hottest summer, highest ocean surface temperature and lowest Antarctic sea ice extent ever. Here is a look at these new climate records and why they matter.
BEST OF EXPRESS