National Suicide Prevention Strategy: Framework and objectives
India National Suicide Prevention Strategy: The government has recently unveiled a national-level suicide prevention plan, the first of its kind. Here are its key features
 According to the annual report of the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), released in August, 1.64 lakh people died by suicide in 2021 -- an increase of 7.2 per cent from 2020. (Wikimedia Commons/Pixabay)
According to the annual report of the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), released in August, 1.64 lakh people died by suicide in 2021 -- an increase of 7.2 per cent from 2020. (Wikimedia Commons/Pixabay)The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare on Monday (November 21) unveiled the National Suicide Prevention Strategy — the first-of-its-kind policy formulated by the government to prevent suicides as a public health priority.
What is India’s National Suicide Prevention Strategy?
According to the ministry, the policy that will set the stage for promotion of mental health and prevention of suicides in the coming decade.
The goal of the strategy is to reduce suicide mortality in the country by 10 per cent by 2023. The strategy provides a framework for multiple stakeholders to implement activities for prevention of suicides in the country.
National Suicide Prevention Strategy: Objectives
There are three main objectives of the strategy.
First, it seeks to establish effective surveillance mechanisms for suicide within the next three years.
Second, it seeks to establish psychiatric outpatient departments that will provide suicide prevention services through the District Mental Health Programme in all districts within the next five years.
Third, it aims to integrate a mental well-being curriculum in all educational institutions within the next eight years.
The fourth objective of the National Suicide Prevention Strategy is to strengthen surveillance of suicide and further generation of evidence through evaluation, that will ensure improvement in the programme quality.
Stakeholders in implementation framework
The implementation framework of the National Suicide Prevention Strategy envisions five key stakeholders responsible for realising the objectives. These include national-level ministerial stakeholders, state-level governmental stakeholders, district-level governmental stakeholders, NIMHANS-Bangalore and other top mental health institutes, and strategic collaborators.
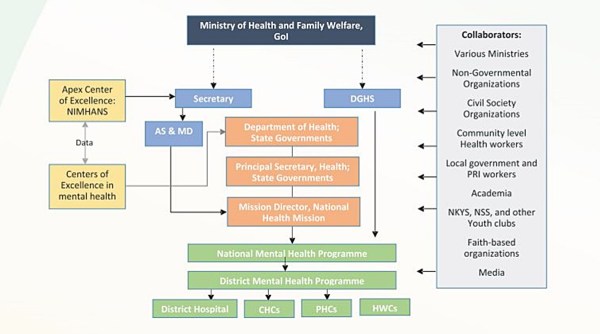 Proposed structure of implementation of the National Suicide Prevention Strategy. (Credit: mohfw website)
Proposed structure of implementation of the National Suicide Prevention Strategy. (Credit: mohfw website)
Implementation mechanism
-Reinforcing leadership, partnerships and institutional capacity in the country
– Enhancing the capacity of health services to provide suicide prevention services
– Developing community resilience and societal support for suicide prevention and reduce stigma associated with suicidal behaviours.
Suicides in India: What’s the current scenario?
According to the annual report of the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), released in August, 1.64 lakh people died by suicide in 2021 — an increase of 7.2 per cent from 2020. This is 10 per cent higher than the COVID deaths (1.48 lakh) in India in 2020, and 6.8 times the maternal deaths (23,800) in the same year.
The NCRB report also stated that more than 1,00,000 people die by suicide in the country every year. A total of 25,891 suicides were reported in the 53 megacities of the country during 2021, with the highest in Delhi.
In the past three years, the suicide rate in the country has increased from 10.2 to 11.3 per 1,00,000 population. Most suicides in India are by youth and middle-aged adults — with 65 per cent of the suicides in 2020 being reported in the age group of 18-45 years.
 Age distribution of suicides in 2020. (Credit: mohfw website)
Age distribution of suicides in 2020. (Credit: mohfw website)
Ongoing suicide prevention initiatives in India
The National Mental Health Policy (2014) sees prevention of mental disorders, reduction of suicide and attempted suicide as core priority areas.
The Mental Healthcare Act 2017 brought in some necessary changes. The Act that came into force from May 2018 effectively decriminalised attempted suicide, which was punishable under Section 309 of the Indian Penal Code. It ensured that the individuals who have attempted suicide are offered opportunities for rehabilitation from the government as opposed to being tried or punished.
Several national programmes such as the National Mental Health Program, National Palliative Care Program, Ayushman Bharat and Nasha Mukti Abhiyaan Task Force are also in place.
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05






































