© IE Online Media Services Pvt Ltd
Latest Comment
Post Comment
Read Comments
 As Budget is a very essentials part of the syllabus of any stage of the competitive exams, especially UPSC, here are the key pointers and highlights of Budget 2024 announcements. Also, don't miss to brush up your basics on budget towards the end of the article.
As Budget is a very essentials part of the syllabus of any stage of the competitive exams, especially UPSC, here are the key pointers and highlights of Budget 2024 announcements. Also, don't miss to brush up your basics on budget towards the end of the article.Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2024 on Tuesday. She highlighted the four main focus points of the first budget under the Modi 3.0 government. It includes: ‘Garib’ (Poor), ‘Yuva’ (Youth), ‘Annadata’ (Farmer) and ‘Nari’ (Women). In her 7th Union Budget speech, finance minister highlighted that this year’s Budget envisages sustained efforts on nine priorities: productivity & resilience in agri, employment & skilling, inclusive human resource development & social justice, manufacturing & services, urban develpoment, energy securities, infrastructure, innovation, R&D and next gen reforms.
As Budget is a very essentials part of the syllabus of any stage of the competitive exams, especially UPSC, here are the key pointers and highlights of Budget 2024 announcements. Also, don’t miss to brush up your basics on budget towards the end of the article.

1. AGRICULTURE
— Allocation: Agriculture and allied sectors were allocated 1.52 Lakh Crore in the Union Budget 2023-24.
— Release of new varieties: The new 109 high-yielding and climate-resilient varieties of 32 field and horticulture crops will be provided to the farmers.
— Natural Framing: In the next two years, 1 crore farmers across the country will be initiated into natural farming. The government will establish 10,000 need-based Bioinput research center.
— Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for Agriculture: The government in partnership with states will facilitate implementation of DPI in three years. The government will enable Jan Samarth-based Kisan Credit cards in five states.
2. EMPLOYMENT AND SKILLING
— The government announced Rs 1.48 lakh crore for education, employment and skill. It will introduce five schemes to provide employment and benefit 4.1 crore youth with an outlay of Rs 2 lakh crores.
— Three new employee-linked incentive schemes will be launched:
(i) Scheme A will support direct benefit transfer of one month salary for first-timers expected to benefit 210 lakh youths.
(ii) Scheme B pertains to job creation in manufacturing. It is expected to benefit 30 lakh youths entering employment, and their employers.
(iii) Scheme C is employer-focussed scheme covering additional employees in all sectors. The scheme is expected to incentivize additional employment of 50 lakh persons.
— The government also announced a new centrally sponsored scheme for skilling in collaboration with states and industry. As part of the scheme, 20 lakh youth will be skilled over five years.
Education
— The government will provide education loans of Rs10 lakh for students for higher education in domestic institutions.
— E-vouchers for this purpose will be given directly to one lakh students every year for annual interest subvention of 3 per cent of the loan amount.
— One thousand industrial training institutes will be upgraded, and the model skill loan scheme will be revised to facilitate loans of up to Rs. 7.5 lakh. This is expected to help 25,000 students a year. Medical colleges and sports institutions will be constructed in Bihar.
Women
— The government announced measures to facilitate higher participation of women in the workforce such as establishment of working women’s hostels and creche facilities.
— Other measures include women-specific skilling programmes and promotion of market access to women-led SHG (Self-Help Groups) enterprises.
— For promoting women-led development, more than Rs 3 lakh crore allocated for schemes benefitting women and girls.
— The government also seeks to encourage states to consider offering lower stamp duty rates for properties purchased by women.
Purvodaya
A plan for the all-round development of the eastern region of the country covering Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and Andhra Pradesh. This will cover human resource development, infrastructure, and generation of economic opportunities to make the region an engine to attain Viksit Bharat.
Amritsar Kolkata Industrial Corridor will support development of an industrial node at Gaya
Development of road connectivity projects, namely (1) Patna-Purnea Expressway, (2) Buxar-Bhagalpur Expressway, (3) Bodhgaya, Rajgir, Vaishali and Darbhanga spurs, and (4) additional 2-lane bridge over river Ganga at Buxar at a total cost of ` 26,000 crore.
Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act
— Special financial support through multilateral development agencies. In the current financial year Rupees 15,000 crore will be arranged, with additional amounts in future years. Full committed to financing and early completion of the Polavaram Irrigation Project. Funds will be provided for essential infrastructure such as water, power, railways and roads in Kopparthy node on the Vishakhapatnam-Chennai Industrial Corridor and Orvakal node on Hyderabad-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor.
Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan
— To be launched for improving the socio-economic condition of tribal communities ( in tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts.)
North East Region
— More than 100 branches of India Post Payment Bank in NER
For MSMEs
— Formulation of a package covering financing, regulatory changes and technology support for MSMEs to help them grow and also compete globally.
— Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs in the Manufacturing Sector ( for purchase of machinery and equipment without collateral or third-party guarantee) and a separately constituted self-financing guarantee fund ( to provide to each applicant, guarantee cover up to ` 100 crore)
— New assessment model for MSME credit — Public sector banks will build their in-house capability to assess MSMEs for credit, instead of relying on external assessment.
— Credit Support to MSMEs during Stress Period — being in the ‘special mention account’ (SMA) stage for reasons beyond their control, MSMEs need credit to continue their business and to avoid getting into the NPA stage.
— For those entrepreneurs who have availed and successfully repaid previous loans under the ‘Tarun’ category — the limit of Mudra loans will be enhanced to Rupees 20 lakh from the current Rupees 10 lakh
— Reduction of the turnover threshold of buyers for mandatory onboarding on the TReDS platform from Rupees 500 crore to Rupees 250 crore.
— SIDBI will open new branches to expand its reach to serve all major MSME clusters within 3 years, and provide direct credit to them.
— Financial support for setting up of 50 multi-product food irradiation units and setting up of 100 food quality and safety testing labs with NABL accreditation will be facilitated.
— E-Commerce Export Hubs will be set up in public-private-partnership (PPP) mode– to enable MSMEs and traditional artisans to sell their products in international markets.
For promotion of Manufacturing & Services
— Internship in 500 top Companies for 1 corore youth in 5 years. (Companies will be expected to bear the training cost and 10 per cent of the internship cost from their CSR funds.)

— Government to facilitate development of investment-ready “plug and play” industrial parks with complete infrastructure in or near 100 cities, in partnership with the states and private sector. (Also look at National Industrial Corridor Development Programme)
— Rental housing with dormitory type accommodation for industrial workers .
— Digital Public Infrastructure Applications proposed in the areas of credit, e-commerce, education, health, law and justice, logistics, MSME, services delivery, and urban governance.
— Critical Mineral Mission for domestic production, recycling of critical minerals, and overseas acquisition of critical mineral assets to be set up.
— The services of the Centre for Processing Accelerated Corporate Exit (C-PACE) will be extended.
— Government will launch the auction of the first tranche of offshore blocks for mining.
— An Integrated Technology Platform for IBC eco-system will be set up.
— Appropriate changes to the IBC, reforms and strengthening of the tribunal and appellate tribunals will be initiated to speed up insolvency resolution.
PM-AWAS Yojana Urban 2.0
— The PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0 aims to fulfil the housing requirements of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families through an investment of ₹10 lakh crore.
— This will entail central aid of ₹2.2 lakh crore over the next 5 years.
— A mechanism for interest subsidies to promote loans at affordable rates is also planned.
— In addition, laws and regulations will be implemented to promote efficient and transparent rental housing markets with increased supply.
Water Supply and Sanitation
— In collaboration with state governments and multilateral development banks, we will promote water supply, sewage treatment, and solid waste management projects and services for 100 major cities through bankable initiatives.
— These initiatives will also include the use of treated water for irrigation and the filling of tanks in surrounding localities.
Street Markets
— The success of PM SVANidhi Scheme altered the lives of street vendors. The government plans to assist in the establishment of 100 weekly haats or street food hubs for the next five years.
Stamp Duty
— The states will be encouraged to continue to charge high stamp duty to moderate rates for all, as well as consider further lowering charges for properties purchased by women. It will form an essential component of urban development plans.
Nuclear Energy
— Research and development of small and modular nuclear reactors
The government will partner with the private sector for:
(1) setting up Bharat Small Reactors,
(2) research & development of Bharat Small Modular Reactor, and
(3) research & development of newer technologies for nuclear energy.
| Do you Know |
| As per the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), the SMRs are advanced nuclear reactors with a power generation capacity ranging from less than 30 MWe to 300+ MWe.
SMRs are: Small – physically a fraction of the size of a conventional nuclear power reactor. Modular – making it possible for systems and components to be factory-assembled and transported as a unit to a location for installation. Reactors – harnessing nuclear fission to generate heat for electricity production or direct application. SMRs cover small and medium-sized modular reactors, depending on the countries’ context whose SSCs are designed for factory production and transportation to project site for installation to shorten the construction schedule – aiming for the economy of serial production, e.g., adding power modules as demand arises. |
| Source: NITI Aayog (www.niti.gov.in) |
Solar Power (PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana)
— In accordance with the declaration in the interim budget, the PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana has begun to install rooftop solar plants, allowing 1 crore homes to get free power for up to 300 units per month.

Pumped Storage Policy
— A strategy will be developed to promote pumped storage projects for electricity storage and to facilitate the smooth integration of renewable energy’s increasing share, notwithstanding its variable and intermittent character, into the overall energy mix.
Advanced Ultra Super Critical Thermal Power Plants
— A joint venture between NTPC and BHEL has completed the development of indigenous technology for Advanced Ultra Super Critical (AUSC) thermal power plants, resulting in a full-scale 800 MW commercial plant.
— Additionally, the development of indigenous capacity for producing high-grade steel and other advanced metallurgy materials for these plants will provide significant economic benefits.
Roadmap for ‘hard to abate’ industries
— A strategy for transitioning the ‘hard to abate’ industries from ‘energy efficiency’ to ’emission objectives’ will be developed.
Support to traditional micro and small industries
— An investment-grade energy audit of traditional micro and small enterprises, such as brass and ceramic, will be supported, and financial assistance will be provided to transition them to cleaner types of energy and install energy efficiency measures.
— The strategy will be reproduced in another 100 clusters in the following phase.
— Allocation: The government has allocated 11,11,111 crore for capital expenditure which would be 3.4 per cent of our GDP.
— Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY): Phase IV of PMGSY will be launched to provide all-weather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations.
— Irrigation and flood control: The government through the Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme and other sources, will provide financial support for projects with an estimated costs of 11,500 crore such as the Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and 20 other ongoing and new schemes.
— Tourism: Vishnupad Temple at Gaya and Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya in Bihar will be developed on the lines of Kashi Vishwanath Temple Corridor to transform them into world-class pilgrim and tourist destinations. Comprehensive development strategies for Rajgir (Bihar) and Nalanda (Bihar). Assistance to the development of important destinations in Odisha will be provided.
— Basic research and prototype: The government has decided to operationalise the Anusandhan National Research Fund for basic research and prototype development.
— Space Economy: To expand the space economy by 5 times in the next 10 years, the government has decided to set up a venture capital fund of 1000 crore.
Rural & Urban Land related Reforms
(1) Assignment of Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) or Bhu-Aadhaar for all lands.
(2) Digitization of cadastral maps.
(3) Survey of map sub-divisions as per current ownership.
(4) Establishment of land registry
(5) Linking to the farmers registry.
(6) Land records in urban areas will be digitized with GIS mapping.
Labour-related Reforms
(1) A comprehensive integration of e-shram portal with other portals will facilitate such one-stop solution.
(2) Shram Suvidha and Samadhan portals will be revamped to enhance ease of compliance for industry and trade.
Taxonomy for climate finance
A taxonomy will be developed for climate finance to enhance the availability of capital for climate adaptation and mitigation.
Foreign Direct Investment and Overseas Investment
The rules and regulations for Foreign Direct Investment and Overseas Investments will be simplified to:
(1) Facilitate FDI
(2) Nudge prioritization
(3) Promote opportunities for using Indian Rupee as a currency for overseas investments.
NPS Vatsalya
A plan for contributions by parents and guardians for minors will be started. On attaining the age of majority, the plan can be converted seamlessly into a normal NPS account.
Ease of Doing Business
The government is working on the Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0. to enhance the ease of doing business. States will also be incentivized for implementation of their Business Reforms Action Plans and digitalization.
New Pension Scheme (NPS)
The Committee to review the NPS has made considerable progress in its work. A solution will be evolved which addresses the relevant issues while maintaining fiscal prudence to protect the common citizens.
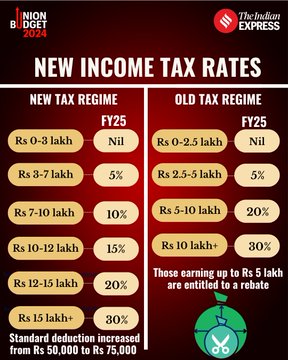
Simplifying New Tax Regime
In the new tax regime, the tax rate structure is proposed to be revised, as follows:
Comprehensive review of Income Tax Act, 1961
— Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced comprehensive review of Income Tax Act, 1961. The purpose is to make the Act concise, lucid, easy to read and understand. This will reduce disputes and litigation, thereby providing tax certainty to the tax payers. It is proposed to be completed in six months.
— A beginning is being made in the Finance Bill by simplifying the tax regime for charities, TDS rate structure, provisions for reassessment and search provisions and capital gains taxation.
Angel Tax Abolished
— Union Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announces the abolishment of angel tax on investors in India, in a bid to boost startups.
— While the angel tax was first introduced in 2012 to deter the generation and use of unaccounted money through the subscription of shares of a closely held company at a value that is higher than the fair market value of the firm’s shares, its scope was widened even to non-resident investors from April 1, 2024 during last year’s Union Budget that saw strong opposition by startups.
Litigation and Appeals
— To dispose of the backlog of first appeals, the Government plan to deploy more officers to hear and decide such appeals, especially those with large tax effect.
— For resolution of certain income tax disputes pending in appeal, the government proposed Vivad Se Vishwas Scheme, 2024.
— To reduce litigation and provide certainty in international taxation, the Government will expand the scope of safe harbour rules and make them more attractive.
Deepening the tax base
For deepening the tax base Security Transactions Tax on futures and options of securities is proposed to be increased to 0.02 per cent and 0.1 per cent respectively.
Other major proposals
— Withdrawal of equalization levy of 2 per cent;
— Expansion of tax benefits to certain funds and entities in IFSCs
— Immunity from penalty and prosecution to benamidar on full and true disclosure so as to improve conviction under the Benami Transactions (Prohibition) Act, 1988.
— Changes in custom duty.
— Simplification and Rationalisation of Capital Gains
What is the Union Budget?
The Union Budget (technically called the Annual Financial Statement under Article 112 of the Constitution of India) lays out an account of the government’s financial health. It tells the citizens not only how much money the government raised last year, where it spent it, and how much it had to borrow to meet the gap, but also gives an estimate of what it expects to earn in the next financial year (in the present case, the current financial year), how much and where it plans to spend it, and how much it would likely have to borrow to bridge the gap. The Revenue and the Capital sections together, make the Union Budget.

What are the important Budget Documents?
Besides the Union Finance Minister’s Budget Speech, various Budget documents are presented to the Parliament.
A.Documents mandated under the constitution of India:
1. Annual Financial Statement (AFS) – Under Art. 112
2. Demands for Grants (DG) — Under Art. 113
3. Finance Bill— Under Art. 110
B. Documents presented as per the provisions of the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003:
1. Macro-Economic Framework Statement
2. Medium-Term Fiscal Policy cum Fiscal Policy Strategy Statement
What are some important terms related to Budget?
1. Revenue Budget: The revenue budget consists of the government’s revenue receipts (Tax revenues and non-tax revenues) and revenue expenditures. Tax revenues comprise proceeds of taxes and other duties levied by the Union.
2. Revenue Expenditure: Revenue expenditure is for the normal running of Government Departments and for rendering of various services, making interest payments on debt, meeting subsidies, 11 grants in aid, etc. Broadly, the expenditure which does not result in the creation of assets for the Government of India is treated as revenue expenditure.
3. Capital Budget: Capital receipts and capital expenditures together constitute the Capital Budget. The capital receipts are loans raised by the Government. Capital expenditure consists of the acquisition of assets like land, buildings, machinery, equipment, as well as investments in shares, etc., and loans and advances granted by the Central Government to the State and the Union Territory Governments, Government companies, Corporations, and other parties.
4. Fiscal Deficit: Fiscal Deficit is the difference between the Revenue Receipts plus Non-debt Capital Receipts (NDCR) and the total expenditure. In other words, fiscal deficit is “reflective of the total borrowing requirements of Government”.
5. Demands for Grants: Article 113 of the Constitution mandates that the estimates of expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of India included in the Annual Financial Statement and required to be voted by the Lok Sabha, be submitted in the form of Demands for Grants.
6. Money Bill: Article 110 defines a “Money Bill” as one containing provisions dealing with taxes, regulation of the government’s borrowing of money, and expenditure or receipt of money from the Consolidated Fund of India, among others.
7. Finance Bill: At the time of presentation of the Annual Financial Statement before the Parliament, a Finance Bill is also presented in fulfillment of the requirement of Article 110 (1)(a) of the Constitution, detailing the imposition, abolition, remission, alteration or regulation of taxes proposed in the Budget. A major difference between money and Financial Bills is that while the latter has the provision of including the Rajya Sabha’s (Upper House) recommendations, the former does not make their inclusion mandatory. The Lok Sabha has the right to reject the Rajya Sabha’s recommendations when it comes to Money Bills.
(Source: http://www.indiabudget.gov.in)
Subscribe to our UPSC newsletter and stay updated with the news cues from the past week.
Stay updated with the latest UPSC articles by joining our Telegram channel – IndianExpress UPSC Hub, and follow us on Instagram and X.

Read UPSC Magazine