More than 1,000 people have been killed in Syria amid clashes between anti-government groups and security forces and a spate of “revenge killings” in one of the deadliest episodes of violence in the country since its civil war erupted 14 years ago. In December, Syria’s long-time leader Bashar al-Assad was unseated by rebel groups. Bashar al-Assad belongs to the Alawite community. The violence coming months after has cast a shadow on the hopes of a stable future for Syria. In this context, let’s know about the Alawites and other communities that have been in the news.
1. Alawite community is a Shia sect of Islam. The Alawites, a minority, had dominated government posts under Assad. The group that has come to power after his fall, Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS), is an al-Qaeda offshoot.
2. Alawites and other Syrian minorities, such as Christians and the Druze, fear they will face persecution under this hardline Sunni regime, although interim President Ahmed al-Sharaa has pledged to carry everyone along. In the government crackdown that followed, scores of civilians were killed. The government forces were joined by armed Sunni fighters, who are reported to have targetted and killed Alawite people in revenge for atrocities under the Assad regime.
1. Turkey has been battling an armed insurgency led by the Kurdistan Workers’ Party, or PKK, a militant group that claims to want better rights for the country’s Kurdish minority. The group initiated a violent insurgency against the Turkish state in the early 1980s, initially seeking independence for the Kurds, who are said to account for 15% or more of Turkey’s population.
 Main Kurdish areas in Middle East.
Main Kurdish areas in Middle East.
2. Kurds are an ethnic group of around 40 million people, with estimates varied greatly. They are centred in Iran, Iraq, Syria, and Turkey. They speak several dialects of Kurdish, a language that is not linked to Turkish or Arabic. The majority are Sunni Muslims.
Story continues below this ad
3. Following World War I, world powers promised the Kurds their own homeland, but this promise was never fulfilled. Kurdish rebellions erupted in numerous nations in subsequent generations, and Kurds’ language and culture were suppressed by the state.
📍Uighurs (China)
1. The United States and other countries made repeated offers to Thailand to resettle more than three dozen Uighurs men before they were deported back to China, where rights groups fear they may face torture and other abuse, the US State Department said Friday (March 7).
2. The Uighurs live in Xinjiang, the largest and most western of China’s administrative regions, which is surrounded by Mongolia, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India. Xinjiang has long had a rebellious and autonomous streak, with the indigenous ethnic Uighurs clashing with the authorities. Uighurs allege the Chinese state has been repressive, clamping down on mosques and religious schools.

3. Uighurs are Muslim, speak a language close to Turkish, and are culturally and ethnically closer to Central Asia than the rest of China.
Story continues below this ad
📍Houthis (Yemen)
1. The Houthis are a large clan belonging to the Zaidi Shia sect, with roots in Yemen’s northwestern Saada province. Zaidis make up around 35 per cent of Yemen’s population.
2. The Zaidis ruled over Yemen for over a thousand years until 1962, when they were overthrown and a civil war followed, which lasted until 1970. The Houthi clan began to revive the Zaidi tradition from the 1980s, resisting the increasing influence of the Salafists, who were funded by the state.
3. Iran, a Shia-majority country, is believed to back the Houthis, even as it has denied the charge. Its regional rival, the Sunni-majority Saudi Arabia (along with Western allies like the US) backs the Yemen government. Houthis’ support for Palestine is, therefore, also a manifestation of existing regional rivalries.
📍Baloch (Pakistan, Iran and Agfhanistan)
1. The 909-km Iran-Pakistan border, known as the Goldsmith Line, stretches from a tripoint with Afghanistan to the northern Arabian Sea. Roughly 9 million ethnic Baloch live on either side of the line, in the Pakistani province of Balochistan, and the Iranian province of Sistan and Baluchestan. Another 500,000 live in the neighbouring areas of Afghanistan in the north.
Story continues below this ad
 Map showing Baloch areas
Map showing Baloch areas
2. The Baloch share cultural, ethnic, linguistic, and religious links that transcend modern borders. They also nurse deeply rooted grievances against both the Pakistani and Iranian states.
3. In Pakistan, the Baloch are an ethnic minority physically and politically distant from the Punjabi-dominated regime; in Iran, in addition to being an ethnic minority, the majority-Sunni Baloch are also a religious minority who have been persecuted by the state.
4. The Baloch homeland is rich in natural resources but impoverished. In Iran, 80% of the Baloch population lives under the poverty line. In Pakistan, massive investments in projects such as China’s Belt and Road initiative have not improved their lives.
5. Baloch nationalism traces its roots to the early decades of the 20th century, when new international borders came to be drawn in the region. Their marginalisation in both countries in subsequent years fuelled several separatist movements for a “Greater Balochistan” nation state.
Story continues below this ad
BEYOND THE NUGGET: What is Levant region?
1. The name “Levant” refers to the historical and geographical subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean Sea to the west and central West Asia, also known as the Middle East.
2. The term “Levant” has its roots in the French word “levant”, meaning “rising” or “to rise”, which refers to the direction of the sunrise in the east. This etymology can be traced further back to the Latin “levare”, which also means “to lift” or “to raise”. The word entered English in 1497 to denote lands along the eastern Mediterranean.
 The highlighted part in the map shows the Levant, which encompasses Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, and Syria, with parts of Iraq, Turkey, and Cyprus also often included. (source – Wikimedia)
The highlighted part in the map shows the Levant, which encompasses Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, and Syria, with parts of Iraq, Turkey, and Cyprus also often included. (source – Wikimedia)
3. The historically rich region of Levant — encompassing Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, and Syria, with parts of Iraq, Turkey, and Cyprus also often included — has long been a crossroads of civilisations. More than just a geographical entity, the Levant embodies layers of history, culture, and identity.
4. Bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west and the Arabian Desert to the east, with the Taurus Mountains in the north and the Sinai Peninsula in the south, its strategic position has made it a vital link between Africa and Eurasia. As a hub of trade, migration, and cultural exchange, the Levant has continuously influenced and been influenced by the world beyond its borders.
Post Read Questions
(1) Consider the following pairs: (UPSC CSE 2016)
Story continues below this ad
|
Community sometimes mentioned in the news |
In the affairs of |
| 1. |
Kurd |
Bangladesh |
| 2. |
Madhesi |
Nepal |
| 3. |
Rohingya |
Myanmar |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
(2) The term “Levant” often heard in the news roughly corresponds to which of the following regions?
(a) Region along the eastern Mediterranean shores
(b) Region along North African shores stretching from Egypt to Morocco
(c) Region along Persian Gulf and Horn of Africa
(d) The entire coastal areas of Mediterranean Sea
Read More:
Over 1,000 killed in Syria in two days: Who is fighting whom, and why
Story continues below this ad
Who are PKK, the Kurdish armed group fighting against Turkey?
Conflicts in West Asia | Levant in turmoil
Explained: Baloch separatism
US says multiple offers were made to resettle Uyghurs before Thailand deported them back to China
🚨Union Budget 2025 special: Click Here to read the February 2025 issue of the UPSC Essentials monthly magazine. Share your views and suggestions in the comment box or at manas.srivastava@indianexpress.com🚨
Subscribe to our UPSC newsletter and stay updated with the news cues from the past week.
Story continues below this ad
Stay updated with the latest UPSC articles by joining our Telegram channel – Indian Express UPSC Hub, and follow us on Instagram and X.



 Main Kurdish areas in Middle East.
Main Kurdish areas in Middle East.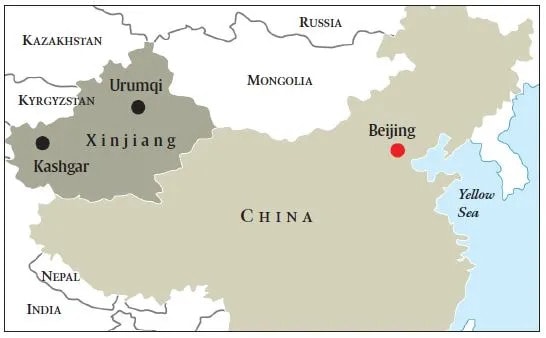
 Map showing Baloch areas
Map showing Baloch areas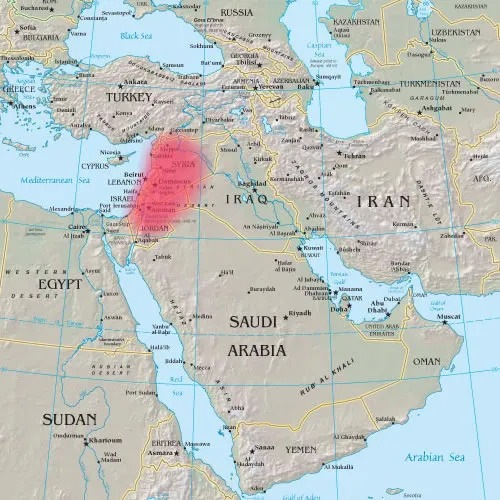 The highlighted part in the map shows the Levant, which encompasses Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, and Syria, with parts of Iraq, Turkey, and Cyprus also often included. (source – Wikimedia)
The highlighted part in the map shows the Levant, which encompasses Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, and Syria, with parts of Iraq, Turkey, and Cyprus also often included. (source – Wikimedia)






























