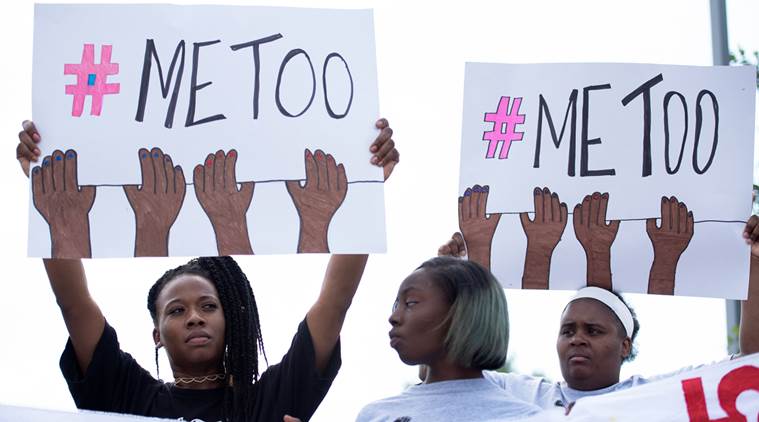 Fast food workers and advocates protest during a demonstration against sexual harassment, at a McDonald’s in St. Louis, (The New York Times image)
Fast food workers and advocates protest during a demonstration against sexual harassment, at a McDonald’s in St. Louis, (The New York Times image)
In a St. Louis suburb, they chanted, “Hold your burgers, hold your fries. Keep your hands off my thighs.” In Chicago, they had blue duct tape that said “MeToo” covering their mouths. And in Kansas City, Missouri, they held signs bearing the same anti-sexual harassment hashtag with the first letter styled to look like the McDonald’s golden arches.
In what organizers said was the first strike in more than 100 years to protest sexual harassment in the workplace, hundreds of McDonald’s employees in those cities and seven others rallied to demand that the largest fast food chain in the country do more to combat the problem.
“We’re protesting today and this is more important than work,” said Kimberly Lawson, explaining that she was skipping her shift to take part in the Kansas City rally. Lawson told the crowd there she had felt “trapped” when a manager made unwanted advances.
“We have the strength to protect one another and demand the justice we deserve,” she said.
Restaurant workers account for a huge slice of the U.S. labour force, with the fast food sector creating more jobs than nearly any other in the past decade. But restaurants typically pay low wages and employ a disproportionate number of young people and women, making those who work in the industry particularly vulnerable to sexual harassment.
The protests Tuesday were organized by Fight for $15, an affiliate of the Service Employees International Union that tries to organize fast food workers and advocates improving their pay and working conditions. In May, 10 McDonald’s employees filed complaints with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, alleging that male supervisors had made unwelcome advances against them and had retaliated against those who complained.
The goal of the protests was to pressure McDonald’s to institute stronger policies to protect workers from sexual harassment at its more than 14,000 stores in the United States. The demands included better training programs for all workers, a more effective way to report complaints and a committee dedicated to addressing sexual harassment issues.
“What McDonald’s does on this issue, how they choose to treat it, how they act on it proactively, will have influence on other stores,” said Mary Joyce Carlson, a lawyer for workers connected to Fight for $15.
In a statement, McDonald’s said it took the issue seriously and was introducing additional measures to provide further protections for workers. The company declined to comment on employment commission complaints, citing “active litigation.”
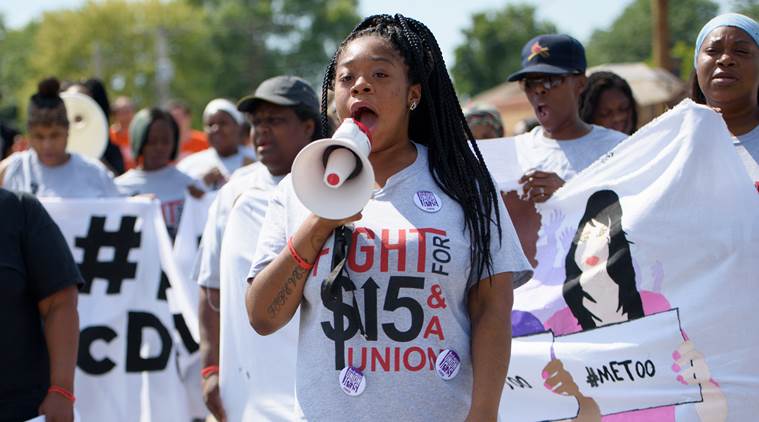 Fast food workers and advocates protest during a demonstration against sexual harassment, at a McDonald’s in St. Louis.(The New York Times photo)
Fast food workers and advocates protest during a demonstration against sexual harassment, at a McDonald’s in St. Louis.(The New York Times photo)
“We have strong policies, procedures and training in place specifically designed to prevent sexual harassment,” the statement said. “To ensure we are doing all that can be done, we have engaged experts in the areas of prevention and response.”
Holding companies accountable for sexual harassment can be difficult. That is especially true in restaurants, where policing bad customer behavior can be particularly hard for workers who depend on tips.
In fast food, the challenges are compounded by the fact that major companies may not consider themselves liable for bad behaviour at individual stores, which are often operated by franchisees who do not always have human resources departments or established procedures for handling sexual harassment complaints.
Employers can be held liable for sexual harassment if victims can show that they were forced to work in a hostile environment where their complaints were ignored or dismissed. In past labour disputes, fast food companies have typically argued that they do not share liability with franchisees who independently own and operate their stores.
Worker advocates counter that companies like McDonald’s dictate everything from menu boards to hiring practices, and should be responsible for adopting effective policies to identify and prevent sexual harassment, too.
“The issue is, how much control is the franchiser exerting over the personnel practices of the franchisee?” said Cynthia Calvert, a discrimination lawyer and senior adviser to the Center for WorkLife Law in San Francisco.
Carlson, the lawyer who works with Fight for $15, suggested McDonald’s had the power to make a broad impact.
“McDonald’s has a huge system, anything it wants to be effective on, it can be,” she said. “The front-line workers, the cooks, the cashiers, as well as people in the management structure, should have a safe place to report a complaint.”
In Chicago, three women who work at a McDonald’s on the city’s South Side were at the protest on Tuesday. One, Brenda Harris, 59, said she had worked at McDonald’s since 1995 and had been groped and harassed too many times to count.
“I’m hoping and praying this is going to change things,” she said.
McDonald’s said in its statement that it had engaged experts like RAINN, the anti-sexual assault nonprofit organization, “to ensure we are doing all that can be done” to combat sexual harassment.
A RAINN spokeswoman said the group had a “preliminary” conversation with McDonald’s several months ago, but had not yet started working with the company.































