Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination: General Studies III: Internal Security
Key Points to Ponder:
• What’s the ongoing story– Ten jawans of the District Reserve Guard (DRG), returning in a van from a security operation, and their driver were killed when Maoists set off an IED in south Chhattisgarh’s Dantewada district, over 350 km from state capital Raipur, on Wednesday afternoon.
• What is LWE? Which states are affected and how has the Government responded?
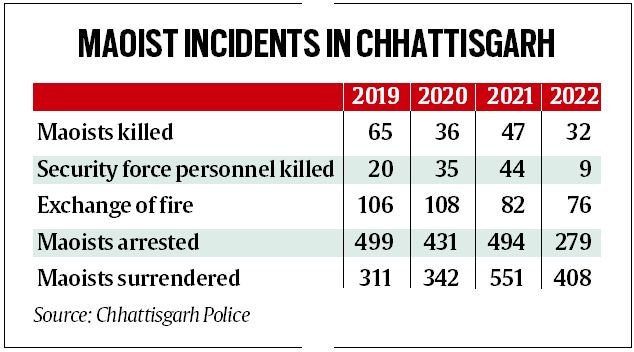
• For your information: This is the biggest attack carried out by Maoists on the security forces in the state in the last two years – in 2021, 22 security personnel were killed in an ambush along the border of Sukma and Bijapur districts.

• Do you know: The timing of the attack is in line with the Maoists’ annual strategy – the CPI (Maoist) conducts Tactical Counter Offensive Campaign (TCOC) between February and June, during which the focus of the military wing is to inflict casualties on security forces.Why is this period is chosen for the attack?
• More on this: From Explained
Why have Maoists killed again — and why do they repeatedly attack in Chhattisgarh?
What is the current LWE situation in the country?
The influence of Maoists and associated violence has been falling consistently in the country because of multiple factors, including a stronger push by security forces in Maoist strongholds, roads and civic amenities reaching the interiors to a greater extent than earlier, and a general disenchantment with the Maoist ideology among the youth, which has deprived the insurgent movement of new leadership.
Story continues below this ad
According to the government, Maoist violence in the country has gone down by 77% since 2010. The number of resultant deaths (security forces + civilians) has come down by 90 % from the all-time high of 1,005 in 2010 to 98 in 2022, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has said.
The government has cut the number of districts declared to be Naxal-affected from over 200 in the early 2000s to just 90 now, and claims that the geographical spread of violence is actually restricted to just 45 districts. The presence of Naxals is said to be minimal to zero in Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Odisha, Jharkhand, and Bihar, which were at one time their strongholds.
According to the MHA, “the arc of violence has been considerably restricted with just 25 districts accounting for 90% of the LWE violence.”
At a press conference last year, Union Home Minister Amit Shah had said that Budha Pahad, a 55 sq km forested area between Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand, considered to be the last bastion of Maoists in Jharkhand, had been freed of the insurgents. Shah has vowed to rid the country of the Maoist problem by 2024.
Why does Chhattisgarh continue to remain troubled?
Story continues below this ad
It is a widely accepted principle in counter-Maoist strategy that the war against Left Wing Extremism can only be won by the state police and not central forces. This is because the state police have local knowledge, understand the language, and have local networks that are essential for the generation of intelligence.
It was through the active involvement of local police in the leading role that states such as Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Odisha and Jharkhand were able to end their Maoist problem. All these states formed special units of their police forces with personnel and officers drawn from the state, gave them special training, and won the battle with concerted security and development efforts.
This process, security establishment sources say, started late in Chhattisgarh. By this time, police of neighbouring states had pushed Maoists from their states to Chhattisgarh, making it a concentrated zone of Maoist influence.
The special unit of the Chhattisgarh Police, the DRG, was raised from the local tribal population and trained to fight Maoists only a few years ago, and has become active relatively recently.
Story continues below this ad
“It is a measure of their activity that in all recent attacks, it is the DRG personnel who have been targeted by the Maoists. We are consistently pushing into Maoist strongholds and conducting intelligence-based operations,” a Chhattisgarh Police officer said.
The absence of roads in the interiors of Bastar has stymied the operations of security forces. Minimal presence of the administration in the interiors of South Bastar has ensured that Maoists continue to have influence in the region and enjoy local support through a mix of fear and goodwill.
• Point to ponder: Over the years, most states affected by Left Wing Extremism have largely tackled the Maoist problem, with state police rather than central forces playing a key role. In Chhattisgarh, various factors make it a challenge. Discuss.
• UPSC CSE (Mains) 2020: What are the determinants of left-wing extremism in the Eastern part of India? What strategy should the Government of India, civil administration and security forces adopt to counter the threat in the affected areas?
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍Fighting Left Wing Extremism in Chhattisgarh, and elsewhere
THE EDITORIAL PAGE
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Story continues below this ad
Mains Examination: General Studies II: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising from their design and implementation.
Key Points to Ponder:
• What’s the ongoing story– In February, the Karnataka state assembly passed amendments to The Factories Act of 1948 to bring flexibility in the labour regime for industry. In April, its neighbouring state, Tamil Nadu also passed similar amendments.
• For your information: The changes carried out, ostensibly aimed to facilitate greater investments by Apple’s vendors such as Foxconn, permit firms to extend the working hours, increase overtime, and allow women to work during night shifts. However, following protests by political parties and labour unions, the state government has now unfortunately put the bill on hold. The attempts by these two states to ease certain contentious provisions of labour laws come at a time when multinational firms are looking to move their production out of China as part of their China plus one strategy in order to reduce their risks.
• Why is it also the job of state governments not only the union government?
Story continues below this ad
• This episode underlines the tricky terrain of labour reform. How? What is the way forward?
• Points to ponder:
What are Labour Reforms? What are four labour codes in India? What is Article 82?
Why our country needs labour reforms and what are the challenges with the new codes?
EXPLAINED
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination: General Studies III: Security Issues
Key Points to Ponder:
• What’s the ongoing story– The manhunt underway in Poonch for the perpetrators of the April 20 ambush on an Army truck that killed five soldiers and badly injured a sixth highlights the importance of securing the border districts of Poonch and Rajouri to the overall terrorist challenge in Jammu & Kashmir. The attack and the subsequent search operation, involving scores of soldiers, drones, and sniffer dogs, recalls an October 2021 ambush on the Army in the same area and a search that stretched over nearly two months. More soldiers were killed before the search came to an end after failing to trace any of the perpetrators of that attack.
• Map work: LAC, Rajouri-Poonch, nearby areas and the demography.
Story continues below this ad
• What have been various incidents in the same areas? Signals through these incidents:
One, that after a gap of almost two decades, cross-border terrorists have set their sights on Jammu once again, perhaps in the hope of exploiting its openly communal atmosphere. Two, their ability to carry out these attacks and melt into the forests indicates support from local communities, which had been hostile to the presence of both foreign and Kashmiri militants from about 2000 onwards.
• What was Operation ‘Sarp Vinash’ and its impact?
• More on this: From The Editorial Page
Pakistan’s old ploy
“A nation on the rise will often lose sight of the ground below.” What does the phrase mean in the context of the subject.
• Two events that spurred the decision to launch the strike- G20 and SCO. Why and how?
• What India should do or ‘must’ not do?
Story continues below this ad
India must not do anything in a hurry despite the cynicism that will aim to target the government. Foreign policy has been well-handled and no major decisions are required when there is an international strategic churn in progress, and nothing major is at stake. Recalibration to balance out the attention between the northern and western borders will ensure greater pragmatism and the proper security focus. The strategic community and the media must assume a larger and more pragmatic role instead of pressuring the government into any hurried decisions.
Operationally, the area south of Pir Panjal perhaps needs a review in terms of the density of troops but the more important imperative pertains to mindsets. The terrain, the target’s proximity to the LoC and a mix of population keep the area in a state of higher vulnerability – it’s this vulnerability that terrorist groups aim to target.
Hopefully, an incident-free May will ensure further security but while the international strategic churn exists and Pakistan’s current status of despair remains, a pragmatic well-thought-out mechanism of response must be evolved — and it need not be only kinetic. The non-kinetic has many options that could help place Pakistan on the mat.
Point to ponder: Terror strike in Poonch flags challenges at the LOC. Discuss.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍Terror strike in Poonch flags challenges at the LOC
📍How revival of Village Defence Committees can play a role
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: General issues on Environmental Ecology, Bio-diversity, and Climate Change – that do not require subject specialization
Mains Examination: General Studies III: Types of Biodiversity, Environment, Conservation, environmental pollution, and degradation, environmental impact assessment
Key Points to Ponder:
• What’s the ongoing story– Global warming is making dangerously hot weather more common, and more extreme, on every continent. A new study by researchers in Britain takes a unique approach to identifying which places are most at risk.
• When the mercury spikes, communities can suffer for many reasons. What are they?
• At a glance: Mitchell and his colleagues looked at maximum daily temperatures around the world between 1959 and 2021. They found that regions covering 31% of Earth’s land surface experienced heat so extraordinary that, statistically, it shouldn’t have happened. These places, the study argues, are now prepared to some degree for future severe hot spells. But there are still many areas that, simply by chance, haven’t yet experienced such extreme heat. So they might not be as prepared. According to the study, these include economically developed places like Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg, plus the region of China around Beijing. But they also include developing countries like Afghanistan, Guatemala, Honduras and Papua New Guinea, that are more likely to lack resources to keep people safe. Other areas at particular risk include far eastern Russia, northwestern Argentina and part of northeastern Australia. Map work!
• What is the significance of the study?
• How to Protect the vulnerable this summer?
• Extreme temperatures threaten public health, the environment and the economy. Right strategies must be put in place. Discuss.
• More on this: FROM THE IDEA PAGE
Indian cities and towns need heat action plans to deal with health challenges posed by global warming: KEEPING IT COOL IN SUMMER
The tragic death of 14 people in Navi Mumbai last week due to heat stroke in a gathering in open ground is a grave reminder of how quickly heat can kill, even in early summer.
You should know: The IMD has predicted a hotter summer this year and we have to take care to prevent as many deaths and heat stroke cases throughout the country as possible. This is doable. Ahmedabad was the first city to start a threshold-based heat action plan (HAP) in 2013, learning from the devastating heat wave of 2010 when, in one week, 800 additional deaths happened in the city.
The IPCC predicts that over the next 80 years, the climate is going to warm up rapidly and relentlessly. The World Meteorological Organization has declared that the past six years have been the hottest globally, indicating the increasing pace of global warming. Hence, it is imperative that all cities, districts and villages in India prepare for heat waves.
• What is Ahemdabad heat action plan?
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍With record-breaking heatwaves, India is sizzling. It is time to act.
THE WORLD
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: General Science
Mains Examination: General Studies III: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
Key Points to Ponder:
• What’s the ongoing story– The discovery of DNA’s double helix structure 70 years ago opened up a world of new science — and also sparked disputes over who contributed what and who deserves credit. Much of the controversy comes from a central idea: that James Watson and Francis Crick — the first to figure out DNA’s shape — stole data from another scientist named Rosalind Franklin.
• Who was Rosalind Franklin? What is the new twist?
• What is Double Helix?
• Know the basics: A complete human genome makes it easier to study genetic variation between individuals or between populations. A genome refers to all of the genetic material in an organism, and the human genome is mostly the same in all people, but a very small part of the DNA does vary between one individual and another. By constructing a complete human genome, scientists can use it for reference while studying the genome of various individuals, which would help them understand which variations, if any, might be responsible for disease.
• DNA and RNA. What is the difference?
• For your information: Genome Mapping
According to the Human Genome Project, there are estimated to be over 20,500 human genes. Genome refers to an organism’s complete set of DNA, which includes all its genes and mapping these genes simply means finding out the location of these genes in a chromosome.
In humans, each cell consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 chromosomes, which means that for 23 pairs of chromosomes in each cell, there are roughly 20,500 genes located on them. Some of the genes are lined up in a row on each chromosome, while others are lined up quite close to one another and this arrangement might affect the way they are inherited. For example, if the genes are placed sufficiently close together, there is a probability that they get inherited as a pair.
Genome mapping, therefore, essentially means figuring out the location of a specific gene on a particular region of the chromosome and also determining the location of and relative distances between other genes on that chromosome.
Significantly, genome mapping enables scientists to gather evidence if a disease transmitted from the parent to the child is linked to one or more genes. Furthermore, mapping also helps in determining the particular chromosome which contains that gene and the location of that gene in the chromosome.
According to the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), genome maps have been used to find out genes that are responsible for relatively rare, single-gene inherited disorders such as cystic fibrosis and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Genetic maps may also point out scientists to the genes that play a role in more common disorders and diseases such as asthma, cancer and heart disease among others.
• Previous Year Question (2019)
‘RNA interference (RNAi)’ technology has gained popularity in the last few years.why?
(1) It is used in developing gene silencing therapies.
(2) It can be used in developing therapies for the treatment of cancer.
(3) It can be used to develop hormone replacement therapies.
(4) It can be used to produce crop plants that are resistant to virtual pathogens.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1 and 4 only
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍What is genome mapping?
📍The complete human genome, and what it tells us
ECONOMY
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination: General Studies III: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
Key Points to Ponder:
• What’s the ongoing story– The European Union (EU) has confirmed the names of 19 platforms that will be subject to its landmark online content rules. Five subsidiaries of Google’s parent Alphabet, two Meta units, two Microsoft businesses, Apple’s AppStore, Twitter, and Alibaba’s AliExpress are among the entities that the EU has identified.
• What is the Digital Services Act (DSA)?
The rules notified under the Digital Services Act (DSA), aim at overhauling the EU’s social media and e-commerce rules, and at tightly regulating the way big technology platforms moderate user content.
• What are the key features of DSA? – Explore on the lines Faster removals and provisions to challenge, Greater responsibility of bigger firms, Direct supervision by the European Commission, transparency, Identifying advertisements.
• EU’s DSA compare with India’s online laws:
India had notified extensive changes to its social media regulations in the form of the Information Technology Rules, 2021 (IT Rules) which placed significant due diligence requirements on large social media platforms such as Meta and Twitter.
India is also working on a complete overhaul of its technology policies and is expected to soon come out with a replacement of its IT Act, 2000, which is expected to look at ensuring net neutrality and algorithmic accountability of social media platforms, among other things.
• What are Social media companies objections?
For your information: The Indian Ministry of Electronics and IT has introduced new rules to safeguard online gamers from addiction and harmful content through a self-regulation model, overseen by SROs. How it will impact the Indian gaming industry?
• New IT rules to put greater obligations on social media platforms to act against unlawful content, misinformation. Do you agree?
• Point to ponder: Government needs to devise regulations to ensure that digital gateways don’t turn into gatekeepers of services and products. How to ensure that the internet remains accessible to all?
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍How to ensure that the internet remains accessible to all
📍What are the EU’s new laws to regulate content online, and how do they compare with India’s?
📍Govt rethinking ‘safe harbour’ in Digital India Bill: How this could change internet landscape
For any queries and feedback, contact manas.srivastava@indianexpress.com
The Indian Express UPSC Hub is now on Telegram. Click here to join our channel and stay updated with the latest Updates.