Astronomers have discovered the roundest known space object
Star, Kepler 11145123 is claimed to be the roundest natural object in space ever as measured by Astronomers
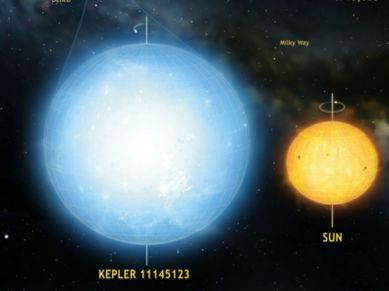
Astronomers claim to have discovered the roundest natural object in space ever measured – a slowly rotating star 5,000 light years away from the Earth. Researchers including Laurent Gizon from the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research and the University of Gottingen in Germany succeeded in measuring the oblateness of the star Kepler 11145123 with unprecedented precision.
The researchers determined stellar oblateness using asteroseismology – the study of the oscillations of stars. The technique showed that the difference between the equatorial and polar radii of the star is only three kilometres (km) – a number that is astonishing small compared to the star’s mean radius of 1.5 million km; which means that the gas sphere is astonishingly round.
NASA’s Kepler mission observed the star’s oscillations continuously for more than four years. Different modes of oscillation are sensitive to different stellar latitudes.
The researchers compared the frequencies of the modes of oscillation that are more sensitive to the low-latitude regions and the frequencies of the modes that are more
sensitive to higher latitudes.
This comparison shows that the difference in radius between the equator and the poles is only three km with a precision of one km. “This makes Kepler 11145123 the roundest natural object ever measured, even more round than the Sun,” said Gizon.
Surprisingly, the star is even less oblate than implied by its rotation rate. The researchers propose that the presence of a magnetic field at low latitudes could make the star look more spherical to the stellar oscillations.
Read: NASA’s ‘impossible’ space engine may actually work
Just like helioseismology can be used to study the Sun’s magnetic field, steroseismology can be used to study magnetism on distant stars. Stellar magnetic fields, especially weak magnetic fields, are notoriously difficult to directly observe on distant stars.
Kepler 11145123 is not the only star with suitable oscillations and precise brightness measurements, researchers said. “We intend to apply this method to other stars observed by Kepler and the upcoming space missions TESS and PLATO. It will be particularly interesting to see how faster rotation and a stronger magnetic field can change a star’s shape,” Gizon added.