© IE Online Media Services Pvt Ltd
Latest Comment
Post Comment
Read Comments
 A man walks past construction vehicles covered in debris caused by flash floods after a lake burst in Rangpo, Sikkim. Attempt a question on Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) in today's answer writing practice. (REUTERS)
A man walks past construction vehicles covered in debris caused by flash floods after a lake burst in Rangpo, Sikkim. Attempt a question on Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) in today's answer writing practice. (REUTERS)UPSC Essentials brings to you its initiative for the practice of Mains answer writing. It covers essential topics of static and dynamic parts of the UPSC Civil Services syllabus covered under various GS papers. This answer-writing practice is designed to help you as a value addition to your UPSC CSE Mains. Attempt today’s answer writing on questions related to topics of GS-1 to check your progress.
What is a Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF)? How GLOF is different from LLOF (Landslide Lake Outburst Flood) in terms of formation and geographical distribution?
How climate change has affected the monsoon rain pattern in India?
Introduction
— The introduction of the answer is essential and should be restricted to 3-5 lines. Remember, a one-liner is not a standard introduction.
— It may consist of basic information by giving some definitions from the trusted source and authentic facts.
Body
— It is the central part of the answer and one should understand the demand of the question to provide rich content.
— The answer must be preferably written as a mix of points and short paragraphs rather than using long paragraphs or just points.
— Using facts from authentic government sources makes your answer more comprehensive. Analysis is important based on the demand of the question, but do not over analyse.
— Underlining keywords gives you an edge over other candidates and enhances presentation of the answer.
— Using flowcharts/tree-diagram in the answers saves much time and boosts your score. However, it should be used logically and only where it is required.
Way forward/ conclusion
— The ending of the answer should be on a positive note and it should have a forward-looking approach. However, if you feel that an important problem must be highlighted, you may add it in your conclusion. Try not to repeat any point from body or introduction.
— You may use the findings of reports or surveys conducted at national and international levels, quotes etc. in your answers.
Self Evaluation
— It is the most important part of our Mains answer writing practice. UPSC Essentials will provide some guiding points or ideas as a thought process that will help you to evaluate your answers.
QUESTION 1: What is a Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF)? How GLOF is different from LLOF (Landslide Lake Outburst Flood) in terms of formation and geographical distribution?
Introduction:
— GLOFs are disaster events caused by the abrupt discharge of water from glacial lakes — large bodies of water that sit in front of, on top of, or beneath a melting glacier.
— Glacial lakes are common in the high elevation of glacierised basin. They are formed when glacial ice or moraines or natural depressions impound water.
— There are several types of such lakes, ranging from melt water ponds on the glacier’s surface to enormous lakes blocked by a glacier in the main valley. Normally, these lakes discharge their water by seepage in front of the retreating glacier.
— The moraine creates a topographic depression in which the melt water is generally accumulated leading to formation of glacial lake. When this lake is watertight, melt waters will accumulate in the basin until seepage or overflow limits the lake level.
Body:
You may incorporate some of the following points in the body of your answer:
| Difference | GLOF | LLOF |
| Formation | Melt water from glaciers generally accumulates to form glacial lakes. The lake is confined by moraine (the deposit of glacial debris) or ice dams. | When a landslide obstructs a river or valley, it forms an impounded lake, which acts as a natural dam. This dam holds back water, creating the lake, until it eventually fails. |
| Geographical distribution | GLOFs are commonly associated with glacial regions in mountainous regions with significant glacial activity. For example, the Himalayas, Andes and Alps. | LLOFs can occur in various geological settings where landslides block rivers or valleys, which can lead to the formation of landslide-dammed lakes. It happens in mountainous regions, but it’s not exclusive to glaciated areas. |
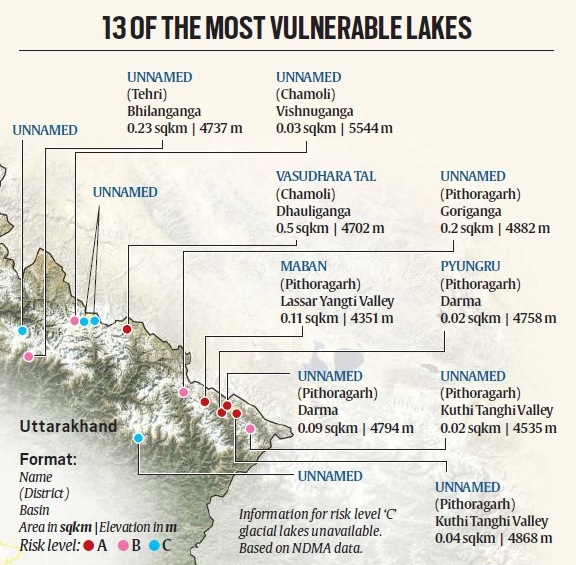 Lakes in Uttarakhand’s Pithoragarh and Chamoli districts are more vulnerable to flooding.
Lakes in Uttarakhand’s Pithoragarh and Chamoli districts are more vulnerable to flooding.
Conclusion:
— The Uttarakhand government has constituted teams of experts to evaluate the risk posed by five potentially hazardous glacial lakes in the region. These lakes are prone to Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs).
— The goal of the risk assessment exercise is to minimise the possibility of a GLOF incident and provide more time for relief and evacuation in case of a breach. Rising surface temperatures across the world, including India, have increased the risk of GLOFs.
(Source: Why Uttarakhand govt wants to evaluate the risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods by Avaneesh Mishra and Alind Chauhan, nidm.gov.in)
Points to Ponder
Difference between floods and flash floods
Lakes and Rivers of Uttarakhand
Related Previous Year Questions
The interlinking of rivers can provide viable solutions to the multi-dimensional inter-related problems of droughts, floods, and interrupted navigation. Critically examine. (2020)
Major cities of India are becoming vulnerable to flood conditions. Discuss. (2016)
QUESTION 2: How climate change has affected the monsoon rain pattern in India?
Introduction:
— There are two notable types of monsoon in India:
(i) Southwest monsoon: It occurs from June to September. It hits Kerala on the southwestern coast and then proceeds across the country. This monsoon is the primary monsoon affecting India — it not only brings respite from the heat but also contributes to the country’s ecosystem and economy, especially the growing of kharif crops.
(ii) Northeast monsoon: It is also known as the retreating monsoon, which occurs from October to December and affects peninsular India. It isn’t as intense as the southwest monsoon but is crucial for the growth of rabi crops.
Body:
You may incorporate some of the following points in the body of your answer:
Effects of climate change on rain pattern in India
— The study, ‘Decoding India’s Changing Monsoon Patterns: A Tehsil-level Assessment’, was carried out by Shravan Prabhu and Vishwas Chitale of the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW), a research and policy think-tank.
— The study found that monsoon patterns in India have been fast-shifting. It is mainly driven by the accelerating rate of climate change.
Findings of the Assessment
— There has been a notable increase in rainfall in the tehsils of traditionally drier areas, like Rajasthan, Gujarat, the Konkan region, central Maharashtra, and parts of Tamil Nadu. These regions witnessed a jump of more than 30% in the southwest monsoon rainfall when compared to the baseline of 1981–2011.
— Meanwhile, traditionally high monsoon rainfall areas such as Assam and Meghalaya saw a reduction in rainfall.
— The southwest monsoon rainfall rose in 55% of India’s tehsils. The increase, however, has resulted from short-duration, severe rainfall, which frequently causes flash floods.
— During the southwest monsoon in India, wet extremes account for an increasing share of total seasonal rainfall.
— Changes in monsoon patterns can affect agriculture output and ecosystems.
— Rainfall is not distributed evenly throughout the seasons and months.
— The retreating monsoon rainfall spiked by more than 10% in approximately 80% of tehsils in Tamil Nadu, 44% in Telangana, and 39% in Andhra Pradesh.
(Source: How India’s monsoon rain pattern has been changing amid climate change by Alind Chauhan)
Points to Ponder
Cropping season
Retreating monsoon
Related Previous Year Questions
Discuss the consequence of Climate change on the food security in tropical countries. (2023)
What characteristics can be assigned to monsoon climate that succeeds in feeding more than 50 percent of the world population residing in Monsoon Asia? (2017)
UPSC Essentials: Mains answer practice — GS 1 (Week 43)
UPSC Essentials: Mains answer practice — GS 1 (Week 44)
UPSC Essentials: Mains answer practice — GS 2 (Week 45)
UPSC Essentials: Mains answer practice — GS 2 (Week 44)
UPSC Essentials: Mains answer practice — GS 3 (Week 45)
UPSC Essentials: Mains answer practice — GS 3 (Week 44)
Subscribe to our UPSC newsletter and stay updated with the news cues from the past week.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LRPvqm7CebU?si=6FV2vahCcUQ9dgvb

Read UPSC Magazine