UPSC Prelims 2024 season has begun, and we are sure you want to have an Express Edge. To ensure your preparations have that extra edge, take a look at the essential concepts, terms, and phenomena from the static and current parts of the UPSC-CSE in our UPSC Essentials’ One word a day. Also don’t miss Point to Ponder and Post Read MCQ which will help you to self-evaluate your retention memory after reading the article.
Subject: Science & Technology, Health
WHY IN NEWS?
— The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) this month granted market authorisation for NexCAR19
— It is India’s first indigenously-developed CAR-T cell therapy, to ImmunoACT, a company incubated by IIT Bombay.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Why is it important?
— This paves the way for the commercial launch of this therapy in India, where it is expected to be available to cancer patients at a tenth of the cost abroad.
What is CAR-T cell therapy?
— Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is a revolutionary therapy that modifies immune cells, specifically T-cells, by turning them into potent cancer fighters known as CAR-T cells.
— T-cells are special cells (white blood cells that find and fight illness and infection) whose primary function is cytotoxic, meaning it can kill other cells.
Story continues below this ad
— In CAR-T therapy, we genetically modify T-cells into cancer-fighting cells. These supercharged cells are then put back into the body, and they go after cancer cells — especially in blood cancers like leukaemia and lymphomas.
How is CAR-T cell therapy different from chemotherapy and immunotherapy?
— While chemotherapy and immunotherapy may add a few months or years to a cancer patient’s life, cell-and-gene therapy is designed to cure and provide lifelong benefit.
— It makes treatment easier with a one-time therapy [unlike several sessions of chemotherapy] that can be truly transformative [for a patient].
— It’s a lifeline for non-responsive cancer patients.
What else you should know?
Story continues below this ad
— NexCAR19 therapy is designed to target cancer cells that carry the CD19 protein. This protein acts like a flag on cancer cells, which allows CAR-T cells to recognise and attach themselves to the cancer cells and start the process of elimination.
— India is now one of the first developing countries to have its indigenous CAR-T and gene therapy platform.
— The therapy is for people with B-cell lymphomas who didn’t respond to standard treatments like chemotherapy, leading to relapse or recurrence of the cancer.
— It causes minimal damage to neurons and the central nervous system, a condition known as neurotoxicity.
Story continues below this ad
— Neurotoxicity can sometimes occur when CAR-T cells recognise the CD19 protein and enter the brain, potentially leading to life-threatening situations.
— The therapy also results in minimal Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), which is characterised by inflammation and hyperinflammation in the body due to the death of a significant number of tumour cells, as CAR-T cells are designed to target and eliminate cancer cells.
— You can think of this like how the body responds to a virus such as SARS-CoV-2, where the immune response triggers an influx of certain proteins called cytokines, causing a lot of inflammation.
(Refer: India’s own CAR-T cell therapy: What is it, when will it be available, and at what cost? by Rahul Purwar, associate professor in the Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering at IIT Bombay and CEO of ImmunoACT. He spoke to Rupsa Chakraborty and Ritika Chopra. )
Story continues below this ad
Beyond the word: What are some of the cutting-edge technologies that have revolutionised cancer care in India?
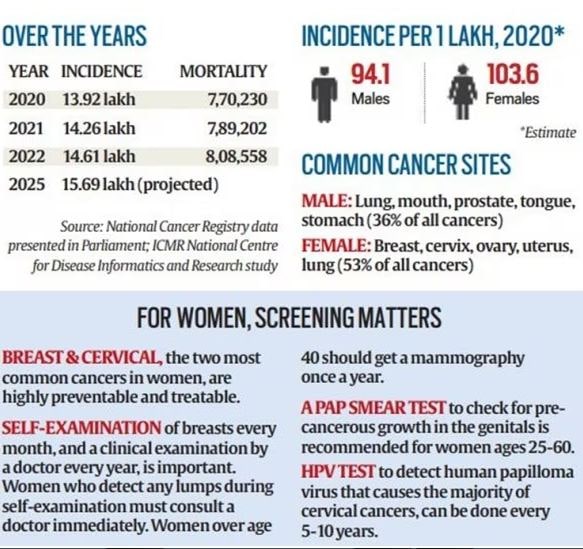
Point to Ponder: Nearly 69 lakh cancer deaths among Indian women were preventable, according to a recent study. Comment.
(Thought Process:
— Around 63% of premature deaths due to cancers in Indian women could have been prevented by reducing risk factors, screening, and diagnosis, while 37% could have been averted with timely and optimal treatment, a new Lancet Commission report on gender inequity in cancer care said.
— Titled ‘Women, Power and Cancer’, the report said around 6.9 million cancer deaths among women in India were preventable and 4.03 million were treatable.
— The report highlighted that even though men are at a higher risk of cancers that affect both genders, cancer incidence and mortality in women remains high. Globally, women account for 48% of the new cancer cases and 44% of cancer deaths. This happens even though some of the cancers in women, such as breast and cervical cancers, are highly preventable and treatable.

Story continues below this ad
— The report said there is a need to regularly collect data on gender and social demographics for cancer health statistics. It called for developing, strengthening, and enforcing laws and policies that reduce exposures to known cancer risks.
— Stating that cancer care and research is dominated by men who decide what is prioritised, funded, or studied, it called for equitable access to cancer research resources, leadership, and funding opportunities for women.
What is behind the poorer outcomes for women?
What is the importance of screening?
What can the government do?)
Post Read MCQ:
Consider the following statements about and answer the question below:
1. The therapy is for people with B-cell lymphomas.
2. The therapy also results in minimal Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS).
Story continues below this ad
3. The therapy is designed to target cancer cells that carry the CD19 protein.
4. The Central Drugs Research Institute (CDRI) granted market authorisation for NexCAR19.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one of the above statements.
(b) Only two of the above statements.
(c) Only three of the above statements.
(d) All of the above statements.
Post your answer in the comment box below.
Share your views and suggestions in the comment box or at manas.srivastava@indianexpress.com