Signs that indicate thyroid related issues
These are six signs you are ignoring that indicate thyroid related issues.
December 18, 2025 14:59 IST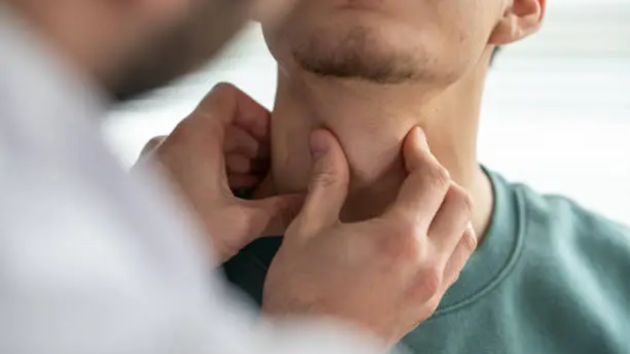 1 / 7
1 / 7The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating energy production, metabolism, body temperature, mood, and many other functions. When it goes out of balance, it can quietly affect different parts of your health. Raymond Douglas MD identifies these signs. Let's have a look at them. (Source: Photo by unsplash)
 2 / 7
2 / 7Persistent Fatigue: If you’re constantly feeling tired or weak, even after enough sleep, that’s a common red flag for thyroid imbalance. For an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), fatigue happens because your metabolism slows down. (Source: Photo by unsplash)
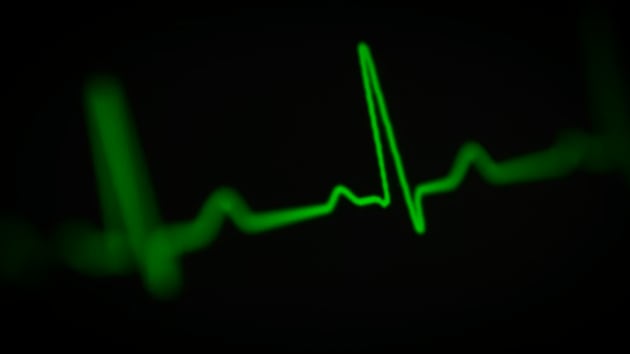 3 / 7
3 / 7Heart Rate and Irregular Heart Beat: A thyroid that is overactive can cause a fast or irregular heartbeat (palpitations), while underactive thyroid may slow down your heart rate. Changes in heart rhythm or unexplained palpitations especially if combined with other signs, are worth checking out medically. (Source: Photo by unsplash)
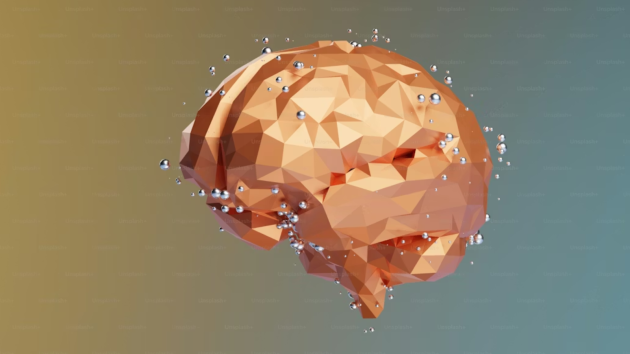 4 / 7
4 / 7Changes in Mood and Memory: Thyroid imbalance can affect your nervous system and brain function leading to mood swings, irritability, depression or what’s often called “brain fog.” Problems with memory, concentration, or mental energy when persistent, may point to thyroid issues. (Source: Photo by unsplash)
 5 / 7
5 / 7Skin, Hair or Temperature Sensitivity Changes: If you notice your skin becoming unusually dry, hair thinning or falling, or feeling excessively cold (with underactive thyroid) or conversely, sweating a lot, feeling too hot, or having heat intolerance (with overactive thyroid) these can be signs your thyroid is out of balance. (Source: Photo by unsplash)
 6 / 7
6 / 7Unexplained Weight Changes: Sudden weight gain, even without changes in diet or activity can signal a sluggish thyroid. On the other hand, unexpected weight loss (despite good appetite) might indicate an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). Either way, unexplained weight change should not be ignored. (Source: Photo by unsplash)
 7 / 7
7 / 7Digestive Issues and Change in Bowel Habits: Thyroid imbalance can slow or speed up your metabolism causing issues such as constipation (often with hypothyroidism) or more frequent bowel movements or diarrhea (often with hyperthyroidism). Persistent digestive changes without obvious cause could hint at thyroid dysfunction. (Source: Photo by unsplash)











