Hidden health risks of consuming excess protein
These are six hidden health risks if you are used to overconsuming protein.
October 31, 2025 19:26 IST 1 / 7
1 / 7Protein is essential for building muscles, repairing tissues, and maintaining overall health. But when consumed in excess, it can silently impact several organs and systems in your body. Here are six hidden health risks you should know. (Source: Photo by unsplash)
 2 / 7
2 / 7Digestive Issues: Too much protein, especially when fibre intake is low, can cause constipation, bloating, and gut imbalance due to reduced intake of fruits and whole grains. (Source: Photo by unsplash)
 3 / 7
3 / 7Heart Health Risks: High protein diets heavy in red or processed meats can increase cholesterol and saturated fat, raising the risk of heart disease over time. (Source: Photo by unsplash)
 4 / 7
4 / 7Dehydration: Protein metabolism requires more water for flushing out waste products. Overeating protein without enough fluids can lead to mild dehydration and fatigue. (Source: Photo by unsplash)
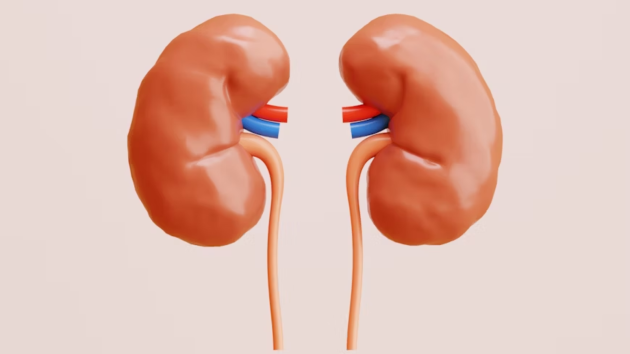 5 / 7
5 / 7Strain on Kidneys: High protein intake, especially from animal sources, increases urea and nitrogen levels, putting pressure on the kidneys, particularly risky for those with pre existing kidney conditions. (Source: Photo by unsplash)
 6 / 7
6 / 7Nutrient Deficiency: Focusing excessively on protein often leads to skipping essential micronutrients like vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that come from plant based foods. (Source: Photo by unsplash)
 7 / 7
7 / 7Weight Gain: While protein helps in short term weight loss, consistently high consumption can lead to caloric surplus and fat storage, reversing the benefits. (Source: Photo by unsplash)











