🚨 The Indian Express UPSC Essentials brings to you the July edition of its monthly magazine. Click Here to read. Share your views and suggestions in the comment box or at manas.srivastava@indianexpress.com🚨
Explained
UPSC Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Polity
Mains Examination: GS-II: Polity
What’s the ongoing story- The Supreme Court has agreed to “take the call” on hearing petitions challenging the “Money Bill route” taken by the government to push through contentious legislation in Parliament.
Prerequisites:
— What is the Money Bill?
— What is the difference between the ordinary Bill and Money Bill?
— How a Money Bill is passed in the Parliament?
Key takeaways:
— Money Bills offer a fast-track route to enact legislation because they do not require passage in Rajya Sabha. Several important laws including amendments to the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002, (PMLA) and the Foreign Contributions Regulations Act, 2010, (FCRA)… have been passed by this route in recent years, circumventing the Upper House.
Story continues below this ad
— In the usual process of lawmaking, a Bill must be passed by majorities in both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. The exceptions are a category of Bills known as Money Bills.
— Under Article 109, a Money Bill shall be introduced only in Lok Sabha and, upon passage, transmitted to Rajya Sabha for its “recommendations”. Rajya Sabha must revert within 14 days, but it is up to Lok Sabha to accept or reject any or all of its recommendations. If the Bill is not returned by Rajya Sabha within the stipulated period, it is considered passed anyway.
— Article 110 provides a strict definition of a Money Bill. In order for a Bill to be designated as a Money Bill, it must contain “only provisions dealing with all or any” of a specific list of subjects.
— Under Article 110(3), “If any question arises whether a Bill is a Money Bill or not, the decision of the Speaker of the House of the People thereon shall be final.”
For Your Information:
Story continues below this ad
— In a general sense, any Bill that relates to revenue or expenditure is a Financial Bill. A Money Bill is also a specific type of Finance Bill, that must deal only with matters specified in Article 110 (1) (a) to (g).
— A Financial Bill becomes a Money Bill when it exclusively falls under one of the seven heads listed under Article 110(1), which defines Money Bills.
Points to Ponder:
— What is the difference between the Finance Bill and Money Bill?
— What are the recent concerns related to the passing of several bills under the Money Bill?
Story continues below this ad
— What are the constitutional provisions related to the Money Bill?
Post Read Question:
Regarding the Money Bill, which of the following statements is not correct? (UPSC CSE 2018)
(a) A bill shall be deemed to be a Money Bill if it contains only provisions relating to the imposition, abolition, remission, alteration or regulation of any tax.
(b) A Money Bill has provisions for the custody of the Consolidated Fund of India or the Contingency Fund of India.
Story continues below this ad
(c) A Money Bill is concerned with the appropriation of money out of the Contingency Fund of India.
(d) A Money Bill deals with the regulation of borrowing of money or giving of any guarantee by the Government of India.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Money Bills vs Finance Bills: What are the differences, what the court has ruled
UPSC Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: GS-II, III: Government initiatives, Science and Technology
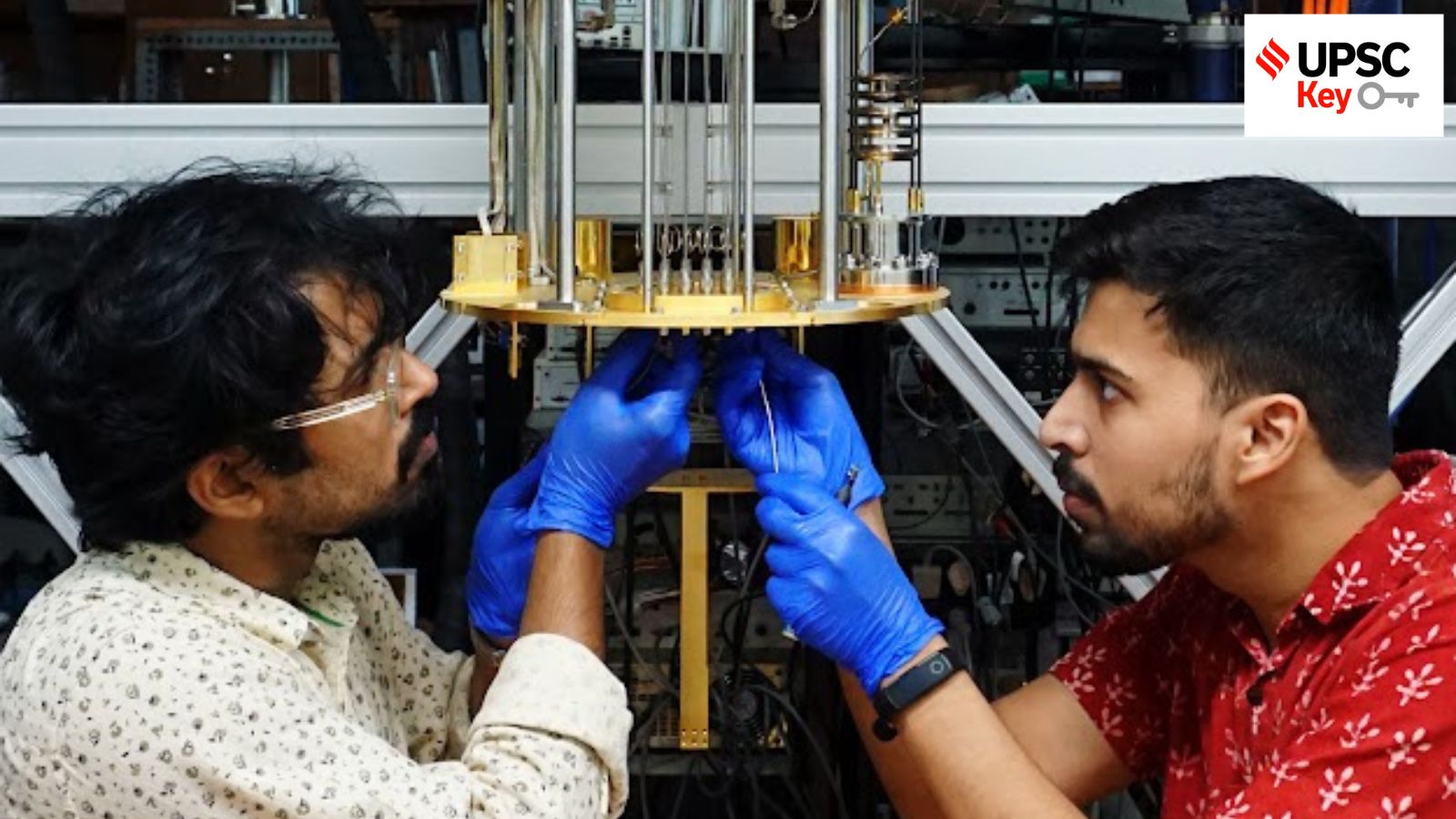
What’s the ongoing story- India launched the National Quantum Mission last year and became one of the few countries in the world to have a dedicated programme to harness the power of quantum technologies. These technologies, which use special properties of the tiniest particles of matter, can yield radical solutions to some of the most intractable problems of our age, such as clean energy and affordable healthcare.
Prerequisites:
— What is ‘quantum’?
— What is the National Quantum Mission?
— What is superposition?
Key takeaways:
Story continues below this ad
— A new report, surveying the existing capabilities of the country in this area, has found that countries like China and the United States have a huge head start over India. These countries have not just invested much more money in funding research, they also have more people working in this sector.
— After several years of discussions, India in 2023 announced the setting up of the National Quantum Mission to build capabilities in quantum-related science and technology. The mission focuses on four key domains: computing, communications, sensors, and materials.
— Quantum technologies try to make use of the fact that matter behaves in a very unexpected and counter-intuitive manner at its smallest scale. Sub-atomic particles such as electrons seemingly exist at multiple locations at the same time, and can influence the behaviour of a like-particle, with which they have had a prior interaction, over infinitely large distances.
— The National Quantum Mission, however, is just the first step and there is a lot of ground to cover, according to the Landscape of Indian R&D in Quantum Technologies report.
Story continues below this ad
— The Rs 6,000 crore (around $0.75 billion) earmarked for the mission is impressive by Indian standards but it pales in comparison to what other countries are spending on quantum-related research, the report said. China is estimated to be investing $15 billion in this effort, while the US is pumping in about $3.75 billion.
— Researchers in China and the US have been producing the largest number of research papers. Between 2000 and 2018, Indian researchers published 1,711 papers on quantum-related science, according to one publicly available database, while Chinese and American researchers published 12,110 and 13,489 papers respectively.
— China and the US are also garnering a lion’s share of the patents being registered… However, Indian researchers had only 339 such patents in the same period, according to a patent database. India was ranked ninth by the number of patents obtained.
Points to Ponder:
— How are quantum computers different from traditional computers?
— What are the challenges of the National Quantum Mission?
— What are the advantages and disadvantages of Quantum technology?
Post Read Question:
Consider the following statements:
1. The property of superposition is the ability of a particle to instantaneously influence the behaviour of another with whom it had an earlier ‘interaction’.
Story continues below this ad
2. Entanglement makes it possible for the quantum bit to exist in both 0 and 1 state simultaneously.
Which of the above statements are not correct?
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
India has large gap to bridge in quantum capabilities
UPSC Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Polity
Mains Examination: GS-II: Government initiatives and interventions
What’s the ongoing story- The Centre has stopped funding for the umbrella program for school education in three opposition-ruled states that have refused to implement its PM SHRI scheme. The Samagra Shiksha Scheme, for which funding has been stopped in West Bengal, Punjab, and Delhi, supports implementation of the Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act, 2009.
Prerequisites:
— What is the PM SHRI scheme?
— What is the Samagra Shiksha Scheme?
— What is the National Education Policy (NEP)?
— What are the constitutional provisions related to education?
Key takeaways:
— PM SHRI scheme was approved in 2022, seeks to develop 14,500 schools to “showcase” the National Education Policy (NEP), 2020, and be “exemplars” for other schools in their region. The scheme is for existing elementary, secondary, and senior secondary schools run by the central government and state and local governments around the country.
— The Centre had declared a total project cost of Rs 27,360 crore for five years until 2026-27, of which the Centre would bear Rs 18,128 crore. At the end of the five-year period, states and Union Territories (UTs) would be required to “continue to maintain the benchmarks achieved by these schools”.
— UP has the most PM SHRI schools (1,865) followed by Maharashtra (910) and Andhra Pradesh (900). No state or local government-run schools in the non-BJP states of Punjab, Delhi, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, West Bengal, and Bihar, as well as Odisha, which got a BJP government only last month, have been included in the scheme.
— PM SHRI schools are selected through the “challenge mode” — schools that meet certain minimum benchmarks (including a pucca building in good condition, barrier-free access ramps, at least one toilet each for boys and girls) can apply online.
— They are evaluated on a set of parameters that include infrastructure, teaching staff, and learning outcomes. Schools in urban areas must score at least 70%; those in rural areas 60% to be selected.
— The state, UT, or Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan/ Navodaya Vidyalaya Samiti is required to sign a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Ministry of Education committing to implement the provisions of the NEP “in entirety within the entire State/ UT”, and to prefix PM SHRI to the name of the selected school.
— Samagra Shiksha, which was proposed by the Union Budget of 2018-19, subsumed the erstwhile Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA), Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA), and Teacher Education (TE) schemes.
— The scheme is funded in a 60:40 ratio by the Centre and states, barring the 11 Northeastern and Himalayan states, which have to bear only 10% of the cost.
Points to Ponder:
— What are the initiatives taken by the government for the implementation of NEP?
— What are the challenges in the education system of India?
— What is the significance of the NEP?
Post Read Question:
Discuss the main objectives of Population Education and point out the measures to achieve them in India in detail. (UPSC CSE 2021)
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
3 Opposition states say no to PM-SHRI, Centre stops school scheme funds
UPSC Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: GS-II, III: Government policies and interventions, Science and technology
What’s the ongoing story- The Gujarat government on Monday (July 15) said that six children have died of suspected Chandipura virus (CHPV) infection in the state since July 10. So far, a total of 12 suspected cases have been reported.
Prerequisites:
— What are viral vectors?
— What are the different types of diseases?
Key takeaways:
— CHPV is a virus of the Rhabdoviridae family, which also includes other members such as the lyssavirus that causes rabies. Several species of sandflies like Phlebotomine sandflies and Phlebotomus papatasi, and some mosquito species such as Aedes aegypti (which is also the vector for dengue) are considered vectors of CHPV.
— The CHPV infection presents initially with flu-like symptoms such as acute onset of fever, body ache, and headache. It may then progress to altered sensorium or seizures and encephalitis.
— The infection can only be symptomatically managed as currently there is no specific antiretroviral therapy or vaccine available for treatment. As a result, it becomes crucial to manage brain inflammation to prevent mortality.
— The CHPV infection was first isolated in 1965 while investigating a dengue/chikungunya outbreak in Maharashtra. However, one of the most significant outbreaks of the disease in India was seen in 2003-04 in states such as Maharashtra, northern Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh, with the three states reporting more than 300 deaths of children.
Points to Ponder:
— What are the diseases caused by mosquitoes?
— What is the government’s vaccination roadmap for these diseases?
— What is the Mission Indradhanush?
Post Read Question:
Consider the following statements: (UPSC CSE 2017)
1. In tropical regions, Zika virus disease is transmitted by the same mosquito that transmits dengue.
2. Sexual transmission of Zika virus disease is possible.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Kerala boy dies due to brain-eating amoeba: What’s it all about and how can it infect you?
Govt & Politics
UPSC Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: GS-II: Government policies and intervention
What’s the ongoing story- The Supreme Court on Monday ruled that states cannot make changes to the Scheduled Caste list published under Article 341 of the Constitution and quashed the 2015 Bihar government notification categorising Tanti-Tantwa community as Scheduled Caste.
Prerequisites:
— What is the Scheduled Caste list?
— Who has the authority to amend the Schedule caste list?
— What is the purpose of Article 341 of the Constitution?
Key takeaways:
— The court said the state government had no competence or authority to tinker with the lists of Scheduled Castes published under Article 341 of the Constitution and directed the group be reverted to its original category of Extremely Backward Class. It called the notification “mala fide” and unpardonable “mischief”.
— The Bihar Legislature had enacted the Bihar Reservation of Vacancies in Posts and Services (for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and other Backward Classes) Act, 1991 (Act No.3 of 1992). Under the Act, it had declared the lists of Extremely Backward Classes and at serial number 33, Tanti-Tantwa was shown as falling under the Extremely Backward Classes.
— In 2011, Bihar government had recommended inclusion of Tanti-Tantwa in the list of SCs as a synonym of “Pan, Sawasi, Panr”.
For Your Information:
— A high-level panel has been formed to examine the administrative steps that can be taken to safeguard the interests of scheduled caste communities like the Madigas.
— The panel will seek to ensure fair allocation of benefits to the most disadvantaged communities within the Scheduled Castes, which have been overshadowed by comparatively affluent and influential groups.
Points to Ponder:
— What is the role of the National Commission for Scheduled Caste?
— Why has the Bihar government classified the Tanti-Tantwa community as a Scheduled Caste?
— What is the power of the state government in classifying a community as Scheduled Caste?
— What are the government initiatives for the upliftment of the Scheduled Caste community?
Post Read Question:
Prelims
Consider the following statements about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India: (UPSC CSE 2019)
1. PVTGs reside in 18 states and one Union Territory.
2. A stagnant or declining population is one of the criteria for determining PVTG status.
3. There are 95 PVTGs officially notified in the country so far.
4. Irular and Konda Reddi tribes are included in the list of PVTGs.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Mains
What are the two major legal initiatives by the state since independence addressing discrimination against Scheduled Tribes (STs)? (UPSC CSE 2017)
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Centre forms committee to examine steps to safeguard interests of SCs
UPSC Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: GS-II: International Relations
What’s the ongoing story- India remains committed to strengthening the critical partnership with Mauritius that is “so important for the future of the Indian Ocean region,” External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar said, on the first day of his two-day visit to Mauritius on Tuesday.
Prerequisites:
— What is the ‘Neighbourhood First Policy’?
— What is the Vision SAGAR?
Key takeaways:
— During his visit, inauguration of 12 High Impact Community Development Projects that are funded by India took place, apart from the exchange of MoUs on education, culture, the digitisation of Immigration Archives and the exchange of Project Plan Documents between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Mauritius Research and Innovation Council (MRIC).
— The visit underscores the importance of the India-Mauritius relationship and is a reflection of India’s ‘Neighbourhood First Policy’, Vision SAGAR, and commitment to the Global South.
For Your Information:
— Mauritius has been on the canvas of renewed diplomatic engagement, particularly Agalega island, a far-flung part of the country more than 1,100km (684 miles) from the main island.
— India’s role in the development of the upgraded airstrip on the Agalega island is well marked, and it allows the Indian Navy to operate P-8I maritime reconnaissance aircraft, which is a significant strategic hook for not just India’s access to the key maritime base, but also a strategic move to counter China, in the wake of its aggressive maritime strategy.
— China’s free trade agreement with Mauritius in early 2021 was swiftly followed by the announcement of India’s comprehensive economic partnership with Mauritius.
Points to Ponder:
— Why is Mauritius important for India?
— What are the economic areas of cooperation in the India-Mauritius relationship?
— What are the recent areas of engagement in the India-Mauritius relationship?
Post Read Question:
Where is Agalega Island located?
(a) Maldives
(b) Mauritius
(c) Sri Lanka
(d) Madagascar
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
PM Modi’s swearing-in ceremony: Signals to India’s neighbourhood and Indian Ocean region
UPSC Ethics and Essay Snippet
‘Wordly Wise’ from The Editorial Page
Music washes away from the soul the dust of everyday life.
— Berthold Auerbach
(Thought Process: German poet Berthold Auerbach wrote in his book “On the Heights”: “… music washes away from the soul the dust of everyday life, and says to each one; ‘thou art now no longer in thine office, or in the barracks, or in thy workshop.'” Recently, a video went viral where a man is seen singing in an overcrowded Mumbai local, and soon the other passengers join in chorus. This is the beauty of music, which takes away the exhaustion of a tireless and long day. The joy of sharing a snatch of a favorite film song or bhajan with fellow sufferers, playing cards or antakshari with strangers, and gossiping with “train friends”: These are what make this inescapable part of most Mumbaikars’ lives a little more bearable. Read more in Yeh Dil Deewana.)
Subscribe to our UPSC newsletter and stay updated with the news cues from the past week.
Stay updated with the latest UPSC articles by joining our Telegram channel – IndianExpress UPSC Hub, and follow us on Instagram and X.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RziHTJ1-4jI?si=dXH_Ey-iRaxJGrqh&w=560&h=315