© IE Online Media Services Pvt Ltd
Latest Comment
Post Comment
Read Comments
 The global gender index ranked India's neighbours Pakistan at 142, Bangladesh at 59, China at 107, Nepal at 116, Sri Lanka at 115 and Bhutan at 103. Know more about various reports for UPSC CSE Prelims. (File Photo)
The global gender index ranked India's neighbours Pakistan at 142, Bangladesh at 59, China at 107, Nepal at 116, Sri Lanka at 115 and Bhutan at 103. Know more about various reports for UPSC CSE Prelims. (File Photo)Are you Prelims ready? UPSC CSE Preliminary Exam 2024 will be conducted on June 16. For aspirants, revision of Current Affairs is one of the most important tasks in the coming days. Here is the checklist of Important Reports and Indexes that every aspirant must learn or revise for their UPSC Prelims.
Published by: World Economic Forum (WEF)
— According to the World Economic Forum’s annual Gender Gap Report, 2023, India has ranked at 127 out of 146 countries in terms of gender parity — an improvement of eight places from last year.
Key takeaways:
— India has attained parity in enrolment across all levels of education.
— India has closed 64.3 per cent of the overall gender gap. However, it underlined that India has reached only 36.7 per cent parity on economic participation and opportunity.
— On political empowerment, India has registered 25.3 per cent parity, with women representing 15.1 per cent of parliamentarians — the highest for the country since the inaugural report in 2006.
— The index ranked India’s neighbours Pakistan at 142, Bangladesh at 59, China at 107, Nepal at 116, Sri Lanka at 115 and Bhutan at 103.
— According to the report, Iceland is the most gender-equal country in the world for the 14th consecutive year and the only one to have closed more than 90 per cent of its gender gap.
Published by: Concern Worldwide and Welthungerhilfe
— India ranked 111th out of 125 countries in the Global Hunger Index 2023. India has a score of 28.7, indicating a serious level of hunger. The country came after neighbouring countries Pakistan (102nd), Bangladesh (81st), Nepal (69th) and Sri Lanka (60th).
Key takeaways:
— According to the report, the rate of undernourishment in India stood at 16.6 per cent and under-five mortality at 3.1 per cent, and the prevalence of anaemia in women aged between 15 and 24 years stood at 58.1 per cent.
— India also has the highest child wasting rate in the world at 18.7 per cent, reflecting acute undernutrition. Wasting is measured based on children’s weight relative to their height.
Issue with the GHI, 2023
— The Women and Child Development Ministry said the index suffers from “serious methodological issues and shows a malafide intent”.
— Three of the four indicators used to calculate the index are connected to children’s health and are therefore not representative of the full population.
— The fourth and most important indicator, ‘Proportion of Undernourished (PoU) population’, is based on an opinion poll with a very small sample size of 3,000 people.
Published by: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
— The 2023 edition of International Migration Outlook analyses recent developments in migration movements and the labour market inclusion of immigrants in OECD countries.
Key takeaways:
— As of June 2023, there were around 4.7 million displaced Ukrainians in OECD countries. Germany, Poland and the United States host the highest number of refugees from Ukraine in absolute terms, while Estonia, the Czech Republic and Lithuania have received the highest number as a share of the population.
— Family migration remained the primary category of entry for new permanent-type migrants, representing 40% of all permanent-type migration.
Published by: World Health Organisation (WHO)
— India accounts for 27 per cent of the total TB cases in the world, according to the recently released Global TB Report 2023 by the World Health Organisation.
Key takeaways:
— The report noted two positive trends for India:
(i) There was an increase in reporting of TB cases, crossing even the pre-pandemic high with 24.2 lakh cases in 2022.
(ii) The coverage of treatment for the infection increased to 80%. The most important data point for India, however, was mortality due to TB.
— A sudden drop in mortality due to TB was noted in the 2023 report.
— India’s TB mortality dropped from 4.94 lakhs in 2021 to 3.31 lakhs in 2022. This resulted in a reduction in India’s contribution towards global mortality from 36 per cent in the previous years to 26 per cent in 2022.
— According to the report, nearly 28.2 lakh people got TB in India in 2022, meaning one person gets TB every 11 seconds in India.
— There has been an increase in reporting of TB cases. The Global TB Report 2023 shows that reporting of cases has improved in India, going beyond the pre-pandemic levels.
— India, along with Indonesia and the Philippines, accounted for 67 per cent decline in reporting of TB cases globally during the pandemic.
— The report also noted that India was the only country to have completed a National TB prevalence survey since 2019.
— India has undertaken several initiatives towards TB elimination including active case finding, scaling up of more accurate molecular testing to block level, screening services made available through the health and wellness centres, and engagement of the private sector as well.
— The Ni-kshay Mitra, where people provide additional nutritional support to TB patients has also resulted in the adoption of over 11 lakh TB patients.
— India has set a target of 2025 for eliminating TB in the country. The national strategic plan 2017-2025 sets the target of no more than 44 new TB cases per lakh population by 2025.
Published by: World Bank
— India has climbed six places on the World Bank’s Logistic Performance Index (LPI) 2023, now ranking 38th in the 139 countries index, as a result of significant investments in both soft and hard infrastructure as well as technology.
— The government announced the PM Gati Shakti initiative, a National Master Plan for multimodal connectivity, in October 2021 to reduce logistics costs and boost the economy by 2024-25.
— In 2022, the prime minister launched the National Logistics Policy (NLP) to ensure quick last-mile delivery, end transport-related challenges, save time and money of the manufacturing sector and ensure desired speed in the logistics sector.
Key takeaways:
— According to the report,
(i) India’s rank moved up five places in infrastructure score from 52nd in 2018 to 47th in 2023.
(ii) India climbed to 22nd spot for international shipments in 2023 from 44th in 2018 and moved four places up to 48th in logistics competence and equality.
— The report quotes modernisation and digitalisation as a reason for emerging economies, like India, to leapfrog advanced countries.
— The report said: “The emerging economies with the shortest delays have gone beyond these packages and have implemented bold tracking and tracing solutions. The dwell time for India is very low (2.6 days).
Published by: UNDP
— GII is a composite metric of gender inequality using three dimensions: reproductive health, empowerment and the labour market.
— A low GII value indicates low inequality between women and men, and vice-versa.
Key takeaways:
— India has been ranked at 108 with a score of 0.437 in 2022. Denmark has topped the index with a score of 0.009.
— The score ranges from 0, where women and men fare equally, to 1, where one gender fares as poorly as possible in all measured dimensions.
Published by: International Energy Agency
— Methane is responsible for around 30% of the rise in global temperatures since the Industrial Revolution, and rapid and sustained reductions in methane emissions are key to limiting near-term global warming and improving air quality.
Key takeaways:
— The energy sector accounts for around 40 per cent of the total average methane emissions from human activity, as oil and natural gas companies are known to release methane into the atmosphere when natural gas is flared or vented.
— More than 260 billion cubic metres (bcm) of natural gas (mostly composed of methane) is wasted through flaring and methane leaks globally. The right policies and implementation can bring 200 bcm of additional gas to markets.
— In the oil and gas sector, emissions can be reduced by over 75 per cent by implementing well-known measures such as leak detection and repair programmes and upgrading leaky equipment.
— 80 per cent of the available options to curb the release of methane could be implemented by the fossil fuel industry at net zero cost.
— Reducing 75 per cent of the wastage of natural gas could lower global temperature rise by nearly 0.1 degree Celsius by mid-century.
Published by: WHO
— Hepatitis is the second leading infectious cause of death globally – with 1.3 million deaths per year, the same as tuberculosis, a top infectious killer.
Key takeaways:
— Viral hepatitis is one of the communicable diseases for which deaths are increasing. About 1.3 million people died of viral hepatitis in 2022, similar to the number of deaths caused by tuberculosis.
— The global coverage of viral hepatitis prevention, diagnosis and treatment is too low, and people living with viral hepatitis and their communities continue to bear the heavy burden of the epidemics.
— Countries have adopted WHO guidelines, but implementation lags behind and the availability of affordable and simplified regimens is limited, especially in primary health care.
— The report presents information on access to health products from 38 WHO focus countries for the viral hepatitis response, which together account for about 80% of the global disease burden of viral hepatitis B and C. Of these, 10 countries – China, India, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Ethiopia, Bangladesh, Viet Nam, Philippines and the Russian Federation – account for nearly two thirds of the burden.
— For hepatitis B, three countries – China, India and Indonesia – represent 50% of the global burden in 2022.
Published by: IQAir
Key takeaways:
— According to a report released by Swiss air quality monitoring body, IQAir, India was declared as the third-most polluted country in 2023, after Bangladesh and Pakistan.
— India had the third worst air quality out of 134 countries in 2023.
— In 2022, India was ranked as the eighth most polluted country with an average PM2.5 concentration of 53.3 micrograms per cubic metre.
— In the report’s list of the top 50 most polluted cities in the world, 42 cities were in India.
Published by: Transparency International
Key takeaways:
— India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on the corruption perceptions index (CPI) for 2023. Denmark has topped the index followed by Finland, New Zealand and Norway.
— The index uses a scale of 0 to 100, where 0 is highly corrupt and 100 is very clean.
— In 2023, India’s overall score was 39 while in 2022, it was 40. India’s rank in 2022 was 85.
— In South Asia, both Pakistan (rank 133) and Sri Lanka (rank 115) are grappling with their respective debt burdens and ensuing political instability.
Published by: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
Key takeaways:
— The Adaptation Gap Report is an annual publication from UNEP, released just ahead of the year-ending climate change conference, and presents the global situation of adaptation to climate change.
— The report for the year 2023 focuses on adaptation finance, or the availability of money to carry out the adaptation projects.
Published by: United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
Key takeaways:
— The declaration, which was also endorsed by Brazil, Ireland, Kenya, Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, and the United Arab Emirates, incorporates an acknowledgement of the substantial risks from potential intentional misuse or unintended issues of control of frontier AI — especially cybersecurity, biotechnology, and disinformation risks, according to the UK government, the summit host.
— The declaration noted the “potential for serious, even catastrophic, harm, either deliberate or unintentional, stemming from the most significant capabilities of these AI models”, as well as risks beyond frontier AI, including those of bias and privacy.
Published by: Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI)
Key takeaways:
— According to the latest report by Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), India was the fourth largest spender globally in 2023 with military expenditure worth $83.6 billion in 2023.
— The latest data showed that the United States, China and Russia remained the top three military spenders globally followed by India and Saudi Arabia.
— According to the report, Indian spending was up by 4.2 per cent from 2022 and by 44 per cent from 2014.
— As per the report, Ukraine became the eighth largest military spender in 2023, increasing its spending by 51%.
Published by: World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
Key takeaways:
— The Global Innovation Index 2023 captures the innovation ecosystem performance of 132 economies and tracks the most recent global innovation trends.
— Switzerland, Sweden, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Singapore lead; China, Turkey, India, Vietnam, the Philippines, Indonesia, and the Islamic Republic of Iran are the middle-income economies that have made the most progress in innovation over the past decade.
— The United States, Singapore and Israel are scoring best in particular innovation indicators.
Published by: FSSAI
— The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has developed the State Food Safety Index to measure the performance of states on various parameters of Food Safety.
— This index is based on performance of State/ UT on five significant parameters, namely, Human Resources and Institutional Data, Compliance, Food Testing – Infrastructure and Surveillance, Training & Capacity Building and Consumer Empowerment.
— The Index is a dynamic quantitative and qualitative benchmarking model that provides an objective framework for evaluating food safety across all States/UTs.
— The scores are calculated on the basis of five parameters with different weightages — ‘Human Resources and Institutional Data’, ‘Compliance’, ‘Food Testing Infrastructure’, ‘Training and Capacity Building’, and ‘Consumer Empowerment’.
— In the 2023 index, a new parameter called ‘Improvement in SFSI Rank’ was added, which assesses improvement in each state’s rank from the year before.
Key takeaways:
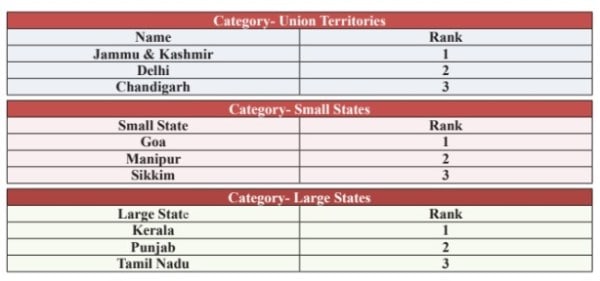
— The steepest fall in scores over five years was seen in Maharashtra, which scored 45 out of 100 in 2023 compared to 74 out of 100 in 2019, followed by Bihar, which scored 20.5 in 2023 compared to 46 in 2019, and Gujarat, which scored 48.5 in 2023 compared to 73 in 2019.
— The worst drop has been observed in the ‘Food Testing Infrastructure’ parameter, which was given the fourth highest weightage of 17 per cent in 2023 (20 per cent in previous years).
— The ‘Compliance’ parameter, which was given the highest weightage of 28 per cent in 2023 (30 per cent in previous years), measures licensing and registration of food businesses, inspections conducted, special drives and camps organised, and other such compliance-related tasks carried out by each state’s food safety authority.
 (Source: FSSAI)
(Source: FSSAI)
Published by: Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
Key takeaways:
— The RBI-DPI comprises five broad parameters that enable measurement of deepening and penetration of digital payments in the country over different periods, viz. payment enablers (with 25 per cent weight), payment infrastructure—demand-side factors (10 per cent), payment infrastructure—supply-side factors (15 per cent), payment performance (45 per cent) and consumer centricity (5 per cent).
— DPI is based on multiple parameters and will reflect accurate penetration of various digital payment modes.
— The index is published on a semi-annual basis.
— The RBI-DPI has been constructed with March 2018 as the base period.
Published by: Pratham Education Foundation (NGO)
Key takeaways:
— The Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) is a nationwide citizen-led household survey that provides a snapshot of the status of children’s schooling and learning in rural India.
— The ASER 2023 ‘Beyond Basics’ survey was carried out among 34,745 young respondents in 28 rural districts in 26 states, including two districts each in Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
— It was first implemented in 2005, the ‘basic’ ASER survey was conducted annually until 2014 and switched to an alternate-year cycle in 2016.
— The ‘basic’ ASER collects information about enrollment in pre-school and school for children in the age group of 3 to 16, and assesses children aged 5 to 16 one-on-one to understand their foundational reading and arithmetic abilities.
Status of Leopards in India
Published by: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change of India
Key takeaways:
— According to the ‘Status of Leopards in India, 2022’ report, there are an estimated 13,874 leopards in India, up from 12,852 in 2018.
— Central India and Eastern Ghats has the highest population of leopards (8,820), followed by the Western Ghats (3,596), and the Shivalik Hills and Gangetic Plains (1,109).
— Statewise, Madhya Pradesh boasts of the largest population of leopards (3,907), followed by Maharashtra (1,985), Karnataka (1,879) and Tamil Nadu (1,070).
— The report showed that the Shivalik Hills and Gangetic Plains recorded a worrying 3.4% per annum decline, going down from 1,253 in 2018 to 1,109 in 2022.
Published by: Ministry of Coal, Government of India.
Key takeaways:
— This index was created to provide a benchmark for revenue-sharing contracts being executed after the auctions for commercial mining of coal.
— The NCI had to be introduced as the wholesale price index (WPI) for coal has no component of imported coal.
Reference period – July 2022 to June 2023.
Conducted by: Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation
Key takeaways:
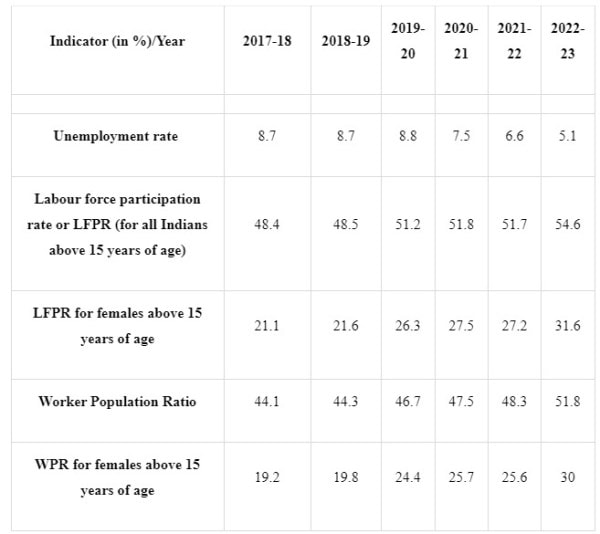
— According to a survey, the unemployment rate among graduates in the age group of 15 years and above has declined to 13.4 per cent in 2022-23 from 14.9 per cent a year ago.
— The lowest unemployment rate among graduates aged 15 years and above witnessed in Chandigarh at 5.6 per cent, which was followed by Delhi with 5.7 per cent during 2022-23.
— The data showed the highest unemployment in Andaman & Nicobar Island at 33 per cent, followed by Ladakh at 26.5 per cent and Andhra Pradesh at 24 per cent.
— Among larger states, the unemployment rate was high in Rajasthan at 23.1 per cent and in Odisha at 21.9 per cent.
Other important Indexes you should know for UPSC CSE Prelims 2024
|
Index |
Published by |
| Travel & Tourism Development Index | World Economic Forum (WEF) |
| World Press Freedom Index (WPFI) | Reporters Without Borders (RSF) |
| Workers and the climate change risk | International Labour Organisation (ILO) |
| Food Waste Index Report 2024 | United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and WRAP (Waste and Resources Action Programme) |
| Finance of Panchayat Raj Institutions | Reserve Bank of India (RBI) |
| State of Global Climate Report, 2023 | World Meteorological Organization (WMO) |
| A World Energy Transitions Outlook Brief: Tracking CoP 28 outcomes” report | International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) |
| Climate Change Performance Index | Germanwatch |
| Human Development Index | United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) |
| World Happiness Report | UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN) |
QUESTION 1
For which of the following indexes, India said the index suffers from “serious methodological issues and shows a malafide intent”?
(a) Global Hunger Index, 2023
(b) Global Gender Report, 2023
(c) International Migration Outlook 2023
(d) Logistic Performance Index
QUESTION 2
With reference to the Global TB Report 2023, consider the following statements:
1. India accounts for about one-fourth of the total TB cases in the world.
2. India’s TB mortality has increased in 2022 as compared to 2021.
3. India is the only country to have completed a National TB prevalence survey since 2019.
4. India has set a target of 2030 for eliminating TB in the country.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
QUESTION 3
Global Methane Tracker 2024 was published by:
(a) World Health Organisation
(b) United Nations Environment Programme
(c) Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
(d) International Energy Agency
QUESTION 4
Consider the following statements about the Global Hepatitis Report:
1. China, India and Indonesia represent half of the global burden for hepatitis B in 2022.
2. It is published by the World Health Organisation.
3. Hepatitis is the second leading infectious cause of death globally.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
QUESTION 5
Consider the following pairs:
| Report | Published by |
| Food Waste Index Report 2024 | Food and Agriculture Organisation |
| Digital Payment Index | International Monetary Fund |
| Logistic Performance Index | World Bank |
How many of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
1. (a)
2. (b)
3. (d)
4. (c)
5. (a)
(Other Sources: http://www.oecd-ilibrary.org, http://www.who.int, http://www.oecd.org, http://www.fssai.gov.in, http://www.rbi.org.in, http://www.wipo.int)
Subscribe to our UPSC newsletter and stay updated with the news cues from the past week.

Read UPSC Magazine