Anonna Dutt is a Principal Correspondent who writes primarily on health at the Indian Express. She reports on myriad topics ranging from the growing burden of non-communicable diseases such as diabetes and hypertension to the problems with pervasive infectious conditions. She reported on the government’s management of the Covid-19 pandemic and closely followed the vaccination programme. Her stories have resulted in the city government investing in high-end tests for the poor and acknowledging errors in their official reports. Dutt also takes a keen interest in the country’s space programme and has written on key missions like Chandrayaan 2 and 3, Aditya L1, and Gaganyaan. She was among the first batch of eleven media fellows with RBM Partnership to End Malaria. She was also selected to participate in the short-term programme on early childhood reporting at Columbia University’s Dart Centre. Dutt has a Bachelor’s Degree from the Symbiosis Institute of Media and Communication, Pune and a PG Diploma from the Asian College of Journalism, Chennai. She started her reporting career with the Hindustan Times. When not at work, she tries to appease the Duolingo owl with her French skills and sometimes takes to the dance floor. ... Read More
Explained: The science behind the cancer cure, and the therapy’s future in India
In a medical trial, 12 patients in the US were completely cured of rectal cancer without requiring any surgery or chemotherapy. A look at the study, and its results
 This fluorescence-colored microscope image shows a culture of cancer cells. (Ewa Krawczyk/National Cancer Institute via AP)
This fluorescence-colored microscope image shows a culture of cancer cells. (Ewa Krawczyk/National Cancer Institute via AP)In a medical trial, results of which were published in The Indian Express on Wednesday, 12 patients in the United States were completely cured of rectal cancer without requiring any surgery or chemotherapy.
The trial used a monoclonal antibody called dostarlimab every three weeks for six months for the treatment of a particular kind of stage two or three rectal cancer. The study was done by doctors from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Centre in New York, and its results have been published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
What are the findings?
The trial showed that immunotherapy alone – without any chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or surgery that have been staples of cancer treatment – could completely cure the patients with a particular kind of rectal cancer called ‘mismatch repair deficient’ cancer”.
All 12 patients had completed the treatment and were followed for six to 25 months after.
“No cases of progression or recurrence had been reported during the follow-up,” the study said. The response too was rapid, with symptoms resolving in 81% of the patients within nine weeks of starting the therapy.
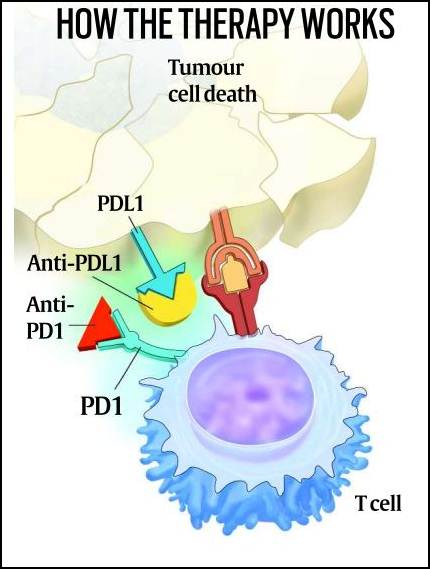 PD1 is a protein that regulates immune function and can sometimes keep T cells from killing cancer cells. The therapy in the trial used PD1 blockades, allowing T cells to kill cancer cells. (Source: National Cancer Institute, US)
PD1 is a protein that regulates immune function and can sometimes keep T cells from killing cancer cells. The therapy in the trial used PD1 blockades, allowing T cells to kill cancer cells. (Source: National Cancer Institute, US)
What is this deficiency, and how was it cured?
‘Mismatch repair deficient’ cancer is most common among colorectal, gastrointestinal, and endometrial cancers. Patients suffering from this condition lack the genes to correct typos in the DNA that occur naturally while cells make copies.
The immunotherapy belongs to a category called PD1 blockades that are now recommended for the treatment of such cancers rather than chemotherapy or radiotherapy. PD1 is a type of protein that regulates certain functions of the immune system, including by suppressing T cell activity, and PD1 blockade therapy looks to release the T cells from this suppression.
“The anomalies in the DNA result in cancerous growths in patients with mismatch repair deficient cancers. If you imagine the immune system to be a car, PD1 acts as the brakes for the T cells of the immune system. By giving the PD1 blockades, we release the brakes and allow the T cells to destroy the cancerous growth,” said Dr P K Julka, former professor of radiotherapy at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi and the current chairman for Max Oncology Daycare Centre. Dr Julka did the first immunotherapy treatment in India while at AIIMS in 2015. He was not involved in the US study.
India has a couple of PD1 blockades available, although not the one used for this study.
If PD1 therapy was already in use, what’s new in the trial?
Earlier, this therapy was used post-surgery, but the study has shown that a surgery may not be required.
“Although the therapy is usually used for cancers that have metastasised (spread to locations other than where the cancer formed), it is now recommended for all mismatch repair deficient cancers as they result in quicker improvement and lesser toxicity as compared to traditional chemo and radiotherapy. So far, we have been using the therapy after a patient undergoes surgery; it is used for 10 to 15 indications. This study shows that even the surgery was not needed in these patients,” Dr Julka said.
Speaking about his own practice, Dr Julka said that in all tumours, they now look for mismatch repair deficiency to see whether immunotherapy can be used.
Eliminating other treatments can improve a patient’s quality of life by preserving fertility, sexual health, and bladder and bowel functions.
When can such a treatment be accessible in India?
Cost is believed to be a major hurdle.
Dr M D Ray, professor of surgical oncology at AIIMS-Delhi, who disagrees with the immunotherapy approach, said: “These patients can be well managed with chemotherapy and radiotherapy as well. Around 10 to 15% of cancer patients actually do not need surgeries. The problem with immunotherapies is that they are expensive and unaffordable for most people in India, and certainly for those coming to AIIMS. A genetic test can also cost up to Rs 30,000, the patients here cannot afford all this.”
He added that precision medicine, such as using particular immunotherapy drugs for particular types of cancers, is still at a nascent stage in India. “Precision medicine for cancer treatment is happening in India, but it is still in nascent stages. It would take at least ten years for it to become commonplace,” he said.
So, how much does immunotherapy cost?
An immunotherapy treatment can cost around Rs 4 lakh per month, with patients needing the treatment for six months to a year.
“People may end up using their life-savings for the treatment. We usually end up giving the treatment only to those who can bank on schemes such as CGHS for sponsoring their treatment or receive free doses from the companies as part of their assistance programme,” said Dr Julka.
However, he added: “One day, cancer will be like any other chronic disease. Like people with diabetes go to work after taking a tablet, cancer patients would too. The future of cancer treatment is molecular oncology – you find a mutation in one gene, you give a particular medicine for it; you find it in another, you give another medicine.”



- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05




































