Stay updated with the latest - Click here to follow us on Instagram
China reports over 7,000 Chikungunya cases, US CDC issues travel warning: Know what is Chikungunya, its symptoms
Chinese health officials have said that the worst affected city in the Guangdong province is the southern city of Foshan with most cases.
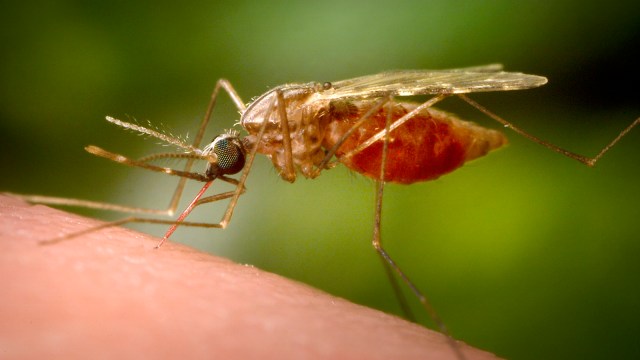 The Chikungunya virus is, however, a rarity in China and the outbreaks are more common in South and South East Asia and parts of Africa. (AP/ File)
The Chikungunya virus is, however, a rarity in China and the outbreaks are more common in South and South East Asia and parts of Africa. (AP/ File)More than 7,000 Chikungunya cases have been reported across China’s Guangdong province since July, triggering the Chinese administration to take measures similar to those taken during the COVID-19 pandemic, BBC reported.
Chinese health officials have said that the worst affected city in the Guangdong province is the southern city of Foshan with most cases. Some of the measures for those affected by the mosquito-borne virus in Foshan include that patients remain in hospital, their beds will be protected with mosquito nets. Patients of Chikungunya cannot leave the hospital until they test negative or after a week-long stay.
The Chikungunya virus is, however, a rarity in China and the outbreaks are more common in South and South East Asia and parts of Africa. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a warning for travellers due to the mosquito-borne virus being transmitted in parts of southeast China.
What is Chikungunya
The Chikungunya disease is caused by the Chikungunya virus which spreads through infected female mosquitoes, most commonly the subspecies Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus, which are the same type of mosquitoes that spread Zika and Dengue virus.
Chikungunya outbreaks have occurred in countries in Africa, Americas, Asia, Europe, the Caribbean, and Indian and Pacific Oceans. In a troublesome update by the US CDC, there is no specific treatment for chikungunya.
When a mosquito feeds on an infected person, it ingests the virus and can transmit it to other humans. The onset of the virus is usually four to eight days after the infected mosquito bites the person. People with risk of more severe disease include newborns infected around the time of birth, older adults (65 years or older), and people with medical conditions such as diabetes or heart disease.
Symptoms of Chikungunya
Those infected with Chikungunya virus typically show symptoms 3-7 days after a bite by an infected mosquito. The most common symptoms are fever and joint pain. According to WHO, Chikungunya virus can also cause muscle pain, headaches, nausea and rashes.
The CDC says most people get better within a week’s time but some can have severe joint pain for months to years following acute illness.
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05































