© IE Online Media Services Pvt Ltd
Latest Comment
Post Comment
Read Comments
 The future of CAR-T cell therapy is promising, with significant potential to further revolutionise cancer treatment. (Representational image via Canva)
The future of CAR-T cell therapy is promising, with significant potential to further revolutionise cancer treatment. (Representational image via Canva)— Amit Kumar
(The Indian Express has launched a new series of articles for UPSC aspirants written by seasoned writers and erudite scholars on issues and concepts spanning History, Polity, International Relations, Art, Culture and Heritage, Environment, Geography, Science and Technology, and so on. Read and reflect with subject experts and boost your chance of cracking the much-coveted UPSC CSE. In the following article, Amit Kumar, a doctoral candidate at IIT Delhi, discusses the challenges in CAR-T cell therapy and the way forward.)
CAR-T cell therapy has shown remarkable success in treating certain cancers. However, there are disadvantages and challenges in the therapy. Some of them are as follows:
1. Severe Side Effects: CAR-T cell therapy can cause severe side effects, the most notable being Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity. CRS occurs when the infused CAR-T cells trigger a massive release of cytokines (small proteins that play a crucial role in cell signalling within the immune system), leading to high fever, nausea, headache, low blood pressure, and, in severe cases, organ failure.
Neurotoxicity can result in confusion, seizures, and other neurological complications. Both conditions – CRS and neurotoxicity – can be life-threatening and often require intensive medical intervention. These side effects necessitate close monitoring and prompt management in a hospital setting, highlighting the need for careful patient selection and preparation before undergoing CAR-T cell therapy.
2. Limited Availability: The therapy requires specialised facilities and expertise, which are not widely available, limiting its accessibility to certain regions and institutions.
3. Variable Efficacy: While CAR-T cell therapy has shown impressive results in many patients, it is not universally effective. Some patients may not respond to the therapy, or their cancer may relapse after an initial period of remission. The reasons for this variability are not fully understood, and more research is needed to identify predictive markers of response and to develop strategies to enhance the durability of the treatment.
4. Tumor Antigen Escape: Some patients who initially respond to CAR-T cell therapy may experience a relapse. This can occur due to the loss or mutation of the targeted antigen on cancer cells, a phenomenon known as antigen escape. As the cancer cells evolve to evade the CAR-T cells, the therapy becomes less effective, posing a significant challenge for long-term disease control.
5. Immunosuppression: Patients may experience prolonged immunosuppression, increasing the risk of infections.
6. Long-Term Effects and Follow-Up: Patients who receive CAR-T cell therapy require extended monitoring for long-term and late side effects, and potential relapses.
Ensuring that there are systems in place for such follow-up care is essential, as is addressing the ethical responsibility of healthcare providers to manage and support patients over the long term.
The way forward
1. Improved Accessibility: Investment in infrastructure and specialised training at more healthcare facilities can expand access to CAR-T cell therapy. In addition, international partnerships can facilitate the sharing of technology and expertise, making CAR-T therapies available in low- and middle-income countries.
2. Enhanced Safety: Developing and implementing standardised protocols for managing side effects like Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity can improve patient outcomes. This includes rapid-response teams and access to necessary medications in these conditions.
3. Increased Efficacy: Developing CAR-T cells that target multiple antigens on cancer cells can reduce the likelihood of antigen escape and improve efficacy. Also, investigating methods to modify the tumor microenvironment to support CAR-T cell activity and persistence can improve therapeutic outcomes.
4. Expanding Applicability: While CAR-T therapy has been highly successful in treating blood cancers, its application to solid tumors remains challenging. Research is focused on identifying suitable targets and overcoming the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.
5. Automation and Accessibility: Streamlining the CAR-T cell production process through automation and standardisation can reduce costs and improve accessibility. Innovations in manufacturing, such as point-of-care production facilities, will make CAR-T therapy more widely available.
6. Integrating emerging technologies: Emerging technologies such as CRISPR/Cas9 (Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein) for precise genetic editing, artificial intelligence for optimising treatment protocols, and synthetic biology for designing novel CAR constructs will drive innovation in CAR-T cell therapy.
The future of CAR-T cell therapy is promising, with significant potential to further revolutionise cancer treatment. Ongoing research, technological innovations, and collaborative efforts within the scientific and medical communities will lead to more effective, safer, and widely accessible CAR-T therapies. As these therapies progress, they offer hope not only for treating a wider variety of cancers but also for addressing other diseases, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life.
India’s first Indigenous CAR-T cell therapy
NexCAR19 CAR-T therapy is developed indigenously in India by IIT Bombay, Tata Memorial Centre, and industry partner immunoACT. India’s first home-grown advanced cell and gene therapy for cancer is the world’s most Affordable CAR-T therapy.
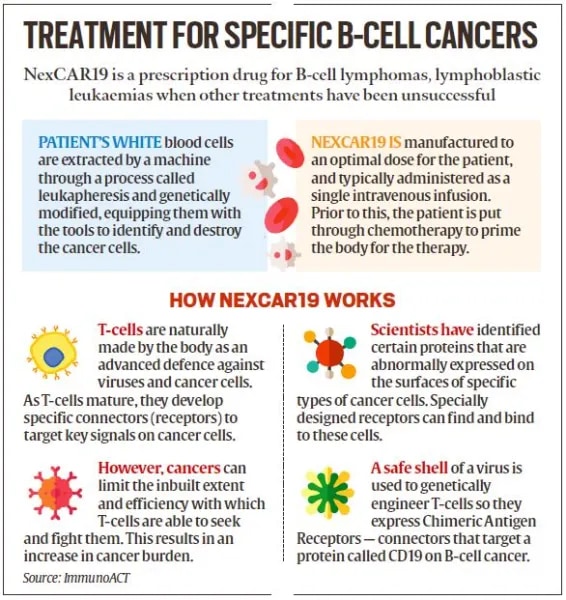
NexCAR19 is designed to target cancer cells carrying the CD19 (Cluster of Differentiation 19) protein, a marker on cancer cells, enhancing precision in treatment.
Initially approved for patients aged 15 and above with B-cell lymphomas (a type of cancer that starts in white blood cells called lymphocytes) who did not respond to standard treatments, leading to relapse or recurrence. Approximately 70% of patients respond to NexCAR19 treatment, with some achieving complete remission.
Lab and animal studies indicate lower drug-related toxicities, including reduced neurotoxicity and Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS). Initially, NexCAR19 was priced at Rs 30-40 lakh. ImmunoACT aims to eventually reduce the cost to Rs 10-20 lakh, making the therapy more accessible.
NexCAR19 is a groundbreaking advancement for India’s medical landscape, reflecting the nation’s growing expertise in biotechnology and personalised medicine. It offers hope for cancer patients and sets a precedent for future innovations in cancer therapy in India.
Post Read Question
Discuss the significance of CAR T-Cell therapy in treating cancer.
What are the disadvantages and challenges in CAR-T cell therapy? Discuss possible solutions.
NexCAR19, a cutting-edge CAR-T cancer therapy developed in India, sets a precedent for future innovations in cancer therapy in India. Comment.
(Amit Kumar is a doctoral candidate at IIT Delhi.)
Subscribe to our UPSC newsletter and stay updated with the news cues from the past week.
The UPSC articles of Indian Express is now on Telegram. Join our Telegram channel- Indian Express UPSC Hub and stay updated with the latest Updates.
Share your thoughts and ideas on UPSC Special articles with ashiya.parveen@indianexpress.com.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nC4ckaj-dJI?si=HiDRY3KyDJMEoY0v&w=560&h=315


